The recent massive data breach highlights a critical vulnerability in the Digital India framework security. 16 billion leaked credentials raise serious concerns about the safety of citizen data stored online. Such breaches not only compromise personal information but also erode public trust in digital platforms, potentially hindering future adoption of digital services.
RESEARCHERS DISCOVERED THE LARGEST DATA BREACH EVER, EXPOSING 16 BILLION LOGIN CREDENTIALS
Researchers announced the discovery of what appears to be the largest data breach ever recorded, with an astonishing 16 billion login credentials exposed. The ongoing investigation, which began earlier this year, suggests that the credentials were collected through multiple infostealer malware strains.
Cybernews researchers who discovered the data leak, reported that tit was composed of 30 massive leaked datasets across various platforms, totaling an unprecedented 16 billion exposed login records.
Cloudflare blocked a massive 7.3 Tbps DDoS attack targeting a hosting provider. A chain of flaws in Linux systems has been found that allows root access to major distributions. The German napkin company Fasana went bankrupt due to a ransomware attack. There has been a significant data breach revealing 16 billion login credentials. The Salt Typhoon group, linked to China, breached the satellite firm Viasat. Iran faced a near-total internet blackout recently. Malicious Minecraft mods aimed to harm gamers, and a data breach at Episource affected 5.4 million people. Veeam fixed a critical bug in its Backup & Replication product. The U. S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added a Linux kernel flaw to its list of known exploited vulnerabilities.
The Flodrix botnet has been targeting vulnerable Langflow servers, while the U. S. CISA noted flaws in Apple products and TP-Link routers. Attackers are now exploiting a vulnerability in Zyxel, and Zoomcar in India faced a data breach impacting 8.4 million users. State-sponsored hackers accessed the email accounts of several Washington Post journalists. A law enforcement operation took down the dark web drug marketplace Archetyp Market. A new ransomware-as-a-service called Anubis includes a wiper module. Predator spyware has shown activity in Mozambique for the first time. Canada’s WestJet airline is dealing with a cyberattack.
Palo Alto Networks has addressed multiple privilege escalation flaws. A unique toolset was used in a recent Fog Ransomware attack, and a cyberattack on United Natural Foods contributed to bread shortages. In Paraguay, a data breach exposed 7.4 million citizens’ records on the dark web. Apple confirmed that a flaw in the Messages app was actively exploited. Trend Micro fixed critical bugs in various products. The Paragon Graphite Spyware utilized a zero-day exploit to hack journalists’ iPhones. Flaws in SinoTrack GPS devices allow unauthorized remote vehicle control. The U. S. CISA added Wazuh and WebDAV flaws to its catalog. Vulnerabilities in 40,000 security cameras can lead to remote hacking.
Operation Secure by INTERPOL took down over 20,000 malicious IP addresses in a significant cybercrime crackdown. A vulnerability in Roundcube Webmail has led to rapid exploitation affecting over 80,000 servers. Another flaw could let unauthorized users recover phone numbers linked to Google accounts, while a data breach at Texas Department of Transportation compromised 300,000 crash reports. The U. S. CISA confirmed critical flaws in multiple systems, and Mirai botnets are exploiting Wazuh vulnerabilities. A China-linked threat actor has targeted over 70 organizations worldwide.
The Department of Justice is trying to seize $7.74 million in cryptocurrency linked to a North Korean scam. OpenAI has banned ChatGPT accounts connected to Russian and Chinese cyber operations. A new Mirai botnet is targeting specific devices, and the BadBox 2.0 botnet has infected millions of IoT devices globally. Recent supply chain attacks on Gluestack packages put over 950,000 weekly downloads at risk. The report also highlighted various cyber threats and attacks affecting organizations and individuals worldwide.
Ref: https://securityaffairs.com/179149/data-breach/researchers-discovered-the-largest-data-breach-ever-exposing-16-billion-login-credentials.html
Digital India Under Scrutiny: A Massive Data Breach Raises Concerns About Mandates and the Enduring Power of Cash
While the “Digital India” initiative promises efficiency and convenience, this data breach serves as a stark reminder of the inherent risks involved. Critics argue that the government’s emphasis on digital mandates, forcing citizens to rely on online platforms for essential services, may have inadvertently created a single point of failure, making the nation more susceptible to large-scale cyberattacks.
The breach raises crucial questions about the security measures in place to protect citizen data. Are current cybersecurity protocols robust enough to withstand increasingly sophisticated attacks? Are government agencies and private companies adequately prepared to handle data breaches and mitigate their impact?
Furthermore, the incident reignites the debate about the role of cash in India’s economy. While digital transactions promote transparency and efficiency, the data breach highlights the inherent security risks associated with storing sensitive information online. For many, the tangible nature and perceived security of cash provide a sense of control and privacy that digital platforms cannot match.
The phrase “Cash is King” resonates strongly in the wake of this breach. It underscores the enduring appeal of physical currency as a safe and reliable alternative to digital transactions, particularly for those who are less digitally literate or concerned about online security. It highlights the need for a balanced approach, one that encourages digital adoption while acknowledging the continued importance of cash in a diverse and complex society.
Impact on Internet Accessibility
Data breaches in India have significant implications for internet accessibility, digital literacy, and financial inclusion. These breaches erode trust in digital systems, potentially discouraging individuals from using online services, which in turn affects digital literacy and financial inclusion efforts.
Data breaches can indirectly affect internet accessibility. If individuals lose trust in the security of online platforms due to breaches, they may be less inclined to use the Internet for financial transactions or other sensitive activities. This can lead to a decrease in internet usage, particularly among those who are less digitally literate and more vulnerable to cyber threats.
Major Data Breaches in India
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing remains a prevalent threat, with cybercriminals using deceptive emails and websites to steal sensitive information.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks are a significant concern, particularly in the financial services sector, disrupting business operations and demanding payment for data recovery.
- Data Breaches: Data breaches are widespread, with numerous organizations suffering leaks of sensitive personal, financial, and medical data.
- Digital Arrest Scams: Cybercriminals impersonate law enforcement officials to extort money from victims.
- AI-Driven Attacks: The rise of artificial intelligence is leading to more sophisticated attacks, including deepfakes and AI-generated content used for fraud.
The report include a 175% surge in phishing attacks targeting India’s financial sector in H1 2024, a 550% increase in deepfake identity fraud cases since 2019, and a projected loss of INR 700 billion (US$8.3 billion) in 2024 due to deepfake identity fraud. The report also highlights the growing trend of artificial intelligence (AI) in the Indian cybercrime landscape, with attackers leveraging AI to make identity-based attacks more sophisticated and pervasive.
The number represents a 175% surge compared to the same period the prior year, underscoring the heightened activity within an increasingly volatile threat landscape. Kaspersky attributes their surge in India to the ongoing digital transformation, and rapid adoption of digital banking, e-commerce and payment platforms in the country
India is experiencing a rise in deepfake identity fraud, with cases surging by 550% since 2019
By 2029, it’s projected to reach a remarkable US$420 billion, growing at an annual growth rate of 31%
In 2025, the report expects artificial intelligence (AI)-driven cyber attacks to become one of the most scalable and adaptable threats, challenging traditional defenses and requiring innovative countermeasures
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated cyber-espionage groups target critical infrastructure and sensitive systems, remaining undetected for extended periods.
Biometric Data Breaches and Concerns
India has experienced a significant rise in data breaches across both the private and public sectors, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals due to its rapid digital adoption and the presence of a shadow economy where sensitive information is traded.
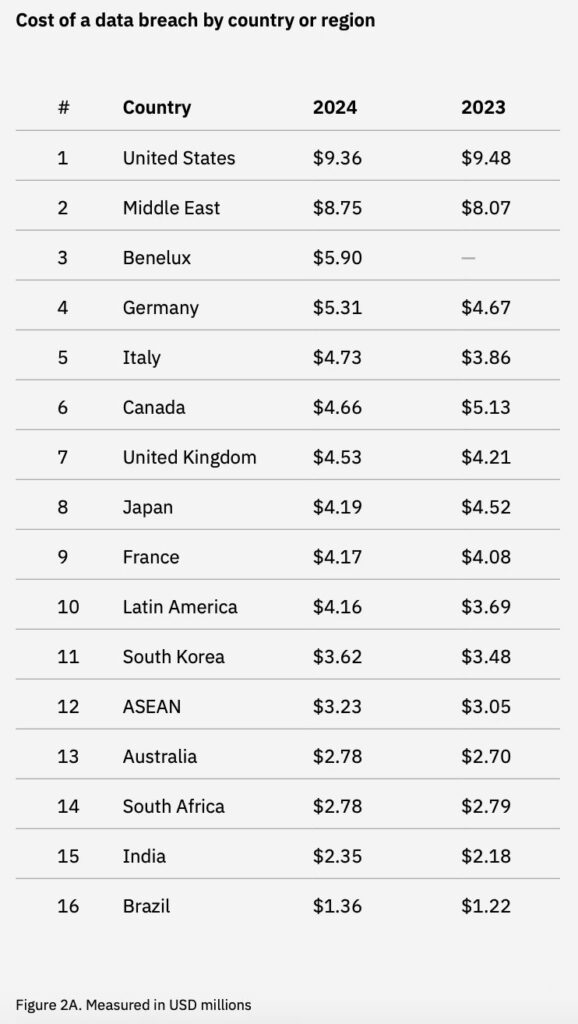
In 2023, India ranked fifth globally in terms of breached accounts, with 5.3 million accounts compromised. The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) reported a massive increase in incidents, from 53,117 in 2017 to 1.32 million between January and October 2023. The financial impact is substantial, with the average cost of a data breach in India reaching $2.18 million in 2023. Phishing and compromised credentials are the most prevalent attack vectors.
Several major data breaches in India have involved the exposure of biometric data:
Major Data Breaches Involving Biometric Data
Biometric data, including fingerprints, facial scans, and iris scans, is particularly sensitive because it is unique and cannot be easily changed. The exposure of such data poses significant risks, including identity theft and impersonation.
Privacy Challenges in Biometric Data Utilization
The utilization of biometric data presents distinct privacy challenges due to its personal nature. Key issues include:
- Unauthorized Secondary Use: One of the significant risks is the potential for biometric data to be used for unintended purposes, leading to privacy breaches and harm. For instance, if fingerprint data collected for authentication is misused for identity theft or unauthorized surveillance.
- Covert Collection Without Consent: Privacy concerns also arise from the covert collection of biometric data in public spaces, such as through cameras or facial recognition technology without individuals’ knowledge. This raises issues of consent, transparency, and control over personal data.
Contributing Factors to Data Breaches
- Aadhaar Data Breach (2018): Breaches involving data, that is linked to many financial services, can expose sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft and financial fraud.
This breach, affecting approximately 1.1 billion residents, exposed extensive personal and biometric information, including names, Aadhaar numbers, bank account details, and biometric data like fingerprints and iris scans . The data was reportedly accessible for a small fee . The World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2019 deemed the Aadhaar breach as the largest data breach in the world .
A major concern highlighted by critics is the accusation that Bill Gates has a hidden agenda to reduce the population in countries such as India, disguised as philanthropic efforts. Through the promotion of programs like Aadhaar and vaccine mandates, Gates is accused of using the Indian population as guinea pigs for his experimental projects.
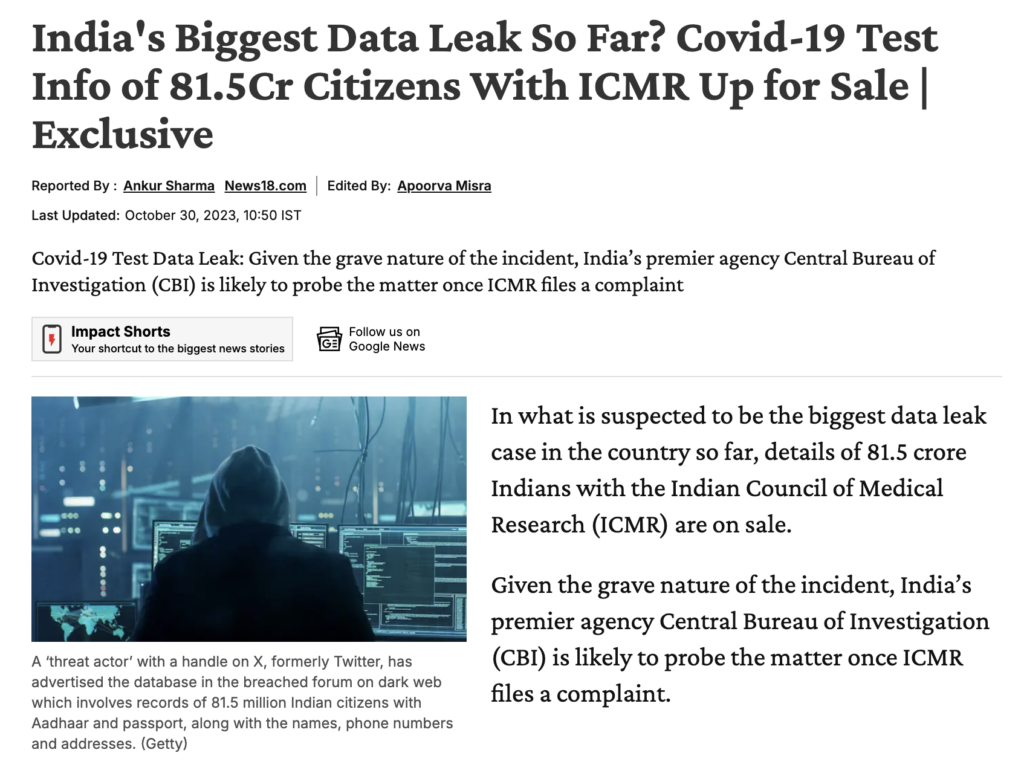
2. ICMR Data Breach (2023): This breach involved the theft of sensitive data belonging to approximately 815 million Indian citizens, including Aadhaar numbers .
3. Data Leak of Police and Military Personnel (2024): A misconfigured database exposed biometric data, including facial scans and fingerprints, of police, military personnel, teachers, and railway workers .
4. Telangana Police’s Hawk Eye Mobile Application (2024): This breach compromised the personal data of approximately 200,000 users, including names, phone numbers, and addresses.

5. Leak of Biometric Police Data in India Signals Rising Risks
A significant data breach in India exposed sensitive biometric information of law enforcement officials and police applicants, including fingerprints and facial images.

The breach was discovered by a security researcher linked to ThoughtGreen Technologies, and the exposed data highlighted the risks associated with storing biometric information. The inability to change biometric details once compromised poses a perpetual risk, and the potential spread and misuse of such data by criminals is a concern. The incident underscores the need for stronger data protection laws and more stringent data handling practices, especially as global reliance on biometric data for identity verification grows.

Indian police adopt facial recognition despite risk of massive data breaches
The rapid adoption of Facial Recognition Technology(FRT) in India raises significant concerns regarding data privacy, security, and potential misuse. These concerns are amplified by the lack of comprehensive data protection laws and the potential for discriminatory application of the technology.
Tamil Nadu: The Tamil Nadu Police were early adopters, deploying a facial recognition system in 2021. This system was developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC) Kolkata.
Meghalaya: The government of Meghalaya is planning to deploy 300 facial recognition cameras and algorithmic software in Shillong to deter criminal activity.
Jammu and Kashmir: Police in Jammu and Kashmir have deployed an AI-based facial recognition system to monitor vehicles on the Jammu-Srinagar National Highway.
Telangana: The Telangana State Police Department is seeking a service provider for its Automated Multimodal Biometric Identification System (AMBIS), which is an upgrade to the existing Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS).
Delhi: Delhi Police also utilizes FRT, with the accuracy of their system being a point of concern.
Maharashtra: Maharashtra is another state where FRT systems are in use.
Bengaluru: Facial recognition software used by the Bengaluru police has identified 2.5 lakh faces with a criminal background in the last 90 days, leading to the arrest of at least 10 people.
The use of FRT by law enforcement raises concerns about potential misuse and the perpetuation of biases.
Technology Providers and Data Security
- Lack of Oversight: There are concerns about the lack of formal criteria for identifying suspects, which could lead to the misuse of FRT.
- Bias in Algorithms: Facial recognition algorithms can be biased, leading to misidentification and disproportionate targeting of certain groups.
- Discrimination: The use of FRT can exacerbate discriminatory policing practices, potentially affecting marginalized communities.
Much of the technology used in India’s FRT systems comes from Japanese companies, such as NEC. While these companies may have human rights policies, the potential for misuse by Indian organizations remains a concern.
The legal and ethical implications of FRT are significant. There is a need for robust regulations to protect privacy and prevent misuse.
Several factors contribute to India’s vulnerability to data breaches:
Prevention Methods
- Rapid Digital Adoption: The swift expansion of digital infrastructure often outpaces the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures, creating security gaps.
- Shadow Economy: The existence of a shadow economy where sensitive personal and financial information is traded exacerbates the risk.
- Outdated IT Infrastructure: Reliance on outdated IT infrastructure and legacy systems makes critical sectors like healthcare, finance, and telecommunications appealing targets.
- Third-Party Vendors: Insufficient vetting and oversight of third-party vendors introduce vulnerabilities.
- Poor API and Endpoint Security: Inadequate security measures for APIs and endpoints allow unauthorized access to data.
- Inadequate Encryption: Weak encryption standards and poor management of user credentials increase the risk of data exposure.
5. UPI Fraud: The Finance Ministry reported a significant increase in fraud incidents related to Unified Payment Interface (UPI) transactions. The data, presented in the Lok Sabha, revealed an 85% rise in fraud cases in FY2023-24 compared to the previous fiscal year.
- FY2022-23: 7.25 lakh cases, totaling Rs 573 crore.
- FY2023-24: 13.42 lakh cases, totaling Rs 1,087 crore.
- FY2024-25 (by September): 6.32 crore fraud cases, amounting to Rs 485 crore.
Ref: https://www.medianama.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Lok-Sabha-Question-Fraud-in-UPI-Transactions.pdf
6. Data Breaches in Financial Institutions: Breaches at banks and fintech companies can lead to the exposure of customer data, resulting in financial losses and a loss of trust in the financial system.
The report include a 175% surge in phishing attacks targeting India’s financial sector in H1 2024, a 550% increase in deepfake identity fraud cases since 2019, and a projected loss of INR 700 billion (US$8.3 billion) in 2024 due to deepfake identity fraud. The report also highlights the growing trend of artificial intelligence (AI) in the Indian cybercrime landscape, with attackers leveraging AI to make identity-based attacks more sophisticated and pervasive.
The number represents a 175% surge compared to the same period the prior year, underscoring the heightened activity within an increasingly volatile threat landscape. Kaspersky attributes their surge in India to the ongoing digital transformation, and rapid adoption of digital banking, e-commerce and payment platforms in the country
Third-Party Risks
Fintech companies often rely on third-party vendors for various services, introducing potential security vulnerabilities. Assessing and managing the cybersecurity posture of third-party partners is crucial to preventing supply chain attacks and data breaches.
Technology Vulnerabilities
Ensuring the security of software applications, APIs, and infrastructure is paramount. Regular vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and timely patch management help in identifying and addressing security weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
In 2022, a prominent Indian fintech startup experienced a significant data breach due to a vulnerability in their API. Attackers exploited this weakness to gain unauthorized access to customer data, including personal identification information and transaction details.
The breach resulted in:
- Financial Losses: Direct financial impact from the breach, including costs associated with remediation, legal fees, and fines.
- Reputation Damage: Erosion of customer trust led to a decline in user base and negative media coverage.
- Regulatory Consequences: The company faced penalties from regulatory bodies for non-compliance with data protection standards.
- BharatPay: In August 2022, BharatPay experienced a serious data breach exposing the personal data of around 37,000 users.
- Policybazaar: The online insurance aggregator, Policybazaar, suffered a data breach in July 2022, exposing sensitive personal details of its customers.
- Star Health Insurance: At the beginning of 2024, hackers leaked customer data from Star Health, an Indian leading health insurance company.
- WazirX: In early 2024, WazirX, a prominent Indian cryptocurrency exchange, faced a significant data breach when one of its multisig wallets, managed by Liminal’s custody services, was compromised, resulting in the theft of over $230 million.
- Others ..
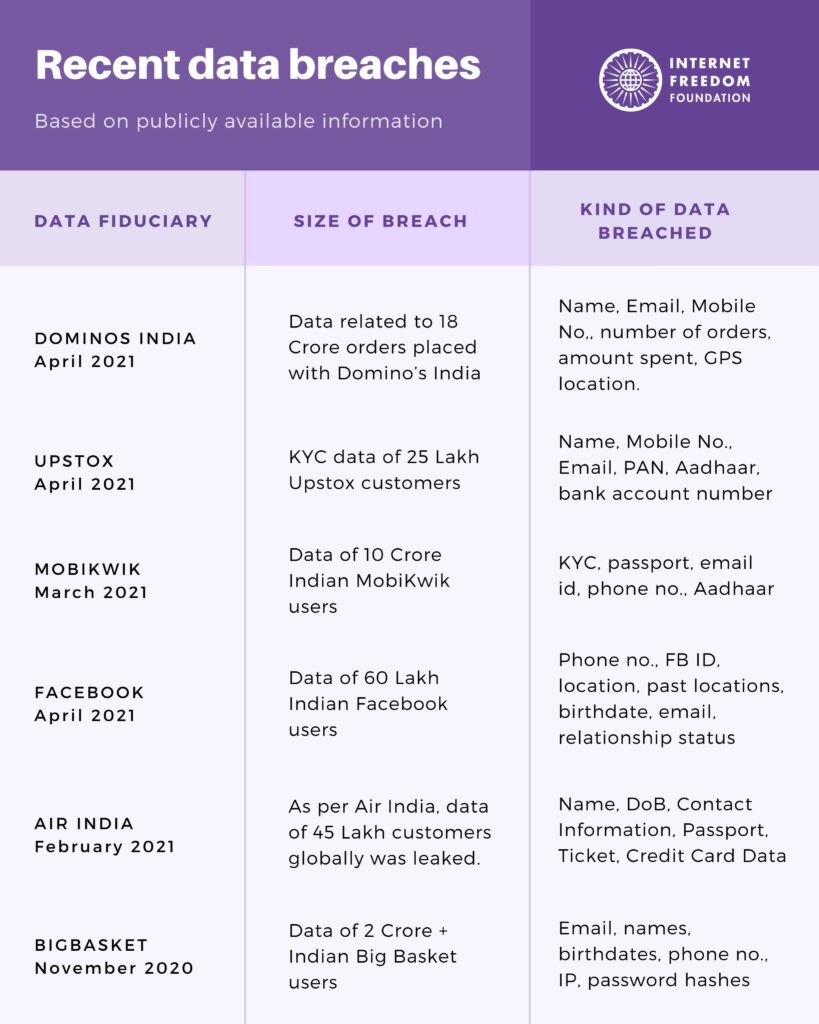
BigBasket Data Breach (2020): Impacted approximately 20 million users, exposing sensitive customer information.
Justdial Data Breach (2019): Exposed the sensitive information of nearly 100 million users.
Hathway Data Breach (2024): Compromised the personal information of over 41.5 million customers.
BSNL Data Breach (2024): Compromised the sensitive data of millions of users.
boAt Data Breach (2024): Exposed sensitive personal data for over 7.5 million customers.
Unacademy Data Breach (2020): Affected over 11 million users.
Types of Cyberattacks
Several high-profile data breaches in recent years highlight the severity of the problem:
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing remains a prevalent threat, with cybercriminals using deceptive emails and websites to steal sensitive information.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks are a significant concern, particularly in the financial services sector, disrupting business operations and demanding payment for data recovery.
- Data Breaches: Data breaches are widespread, with numerous organizations suffering leaks of sensitive personal, financial, and medical data.
- Digital Arrest Scams: Cybercriminals impersonate law enforcement officials to extort money from victims.
- AI-Driven Attacks: The rise of artificial intelligence is leading to more sophisticated attacks, including deepfakes and AI-generated content used for fraud.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated cyber-espionage groups target critical infrastructure and sensitive systems, remaining undetected for extended periods.
To combat the growing cyber threats, organizations and individuals must adopt robust cybersecurity practices:
Prevention Strategies
- Financial Losses: Costs associated with fines, lawsuits, compensation, and remediation.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of customer trust and damage to brand reputation.
- Legal Impacts: Penalties under data protection laws like the Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
- Increased Cybercrime: Stolen data fuels identity theft, financial fraud, and phishing attacks.
- Operational Disruptions: Disruptions to critical services in healthcare, banking, and infrastructure.
Ref:
- Digital India Can’t Do Without the Protective Wall of Cyber Security. [https://www.globalconsultantsreview.com/cxoinsights/digital-india-can-t-do-without-the-protective-wall-of-cyber-security-vid-858.html]
- Data Breaches in India. [ https://www.corbado.com/blog/data-breaches-India ]
- Smoke, Mirrors, and Breaches: What’s Really Happening in India’s Cyber Space. [ https://www.thecore.in/technology/india-cybersecurity-warfare-data-breach-835969 ]
- Understanding India’s Cyber Threat Landscape in 2025. [ https://securityquotient.io/understanding-indias-cyber-threat-landscape-in-2025]
- Biggest Cyber Attacks in India. [ https://www.sattrix.com/blog/biggest-cyber-attacks-in-india/ ]
- Alex. (June 20, 2025). Data Breaches in India: Biggest Breaches, Prevention, and More. [https://www.corbado.com/blog/data-breaches-India]
- India Today. (January 20, 2024). Big data breach threat from Chinese chips in govt biometric attendance. [https://www.indiatoday.in/india-today-insight/story/big-data-breach-threat-from-chinese-chips-in-govt-biometric-attendance-2491261-2024-01-20]
- Hackread.com. (n.d.). Data Leak: Indian Police, Military Biometric Data Exposed. [ https://hackread.com/data-leak-indian-police-military-biometric-data/]
- Fowler, J. (May 23, 2024). Data leak exposes personal data of Indian military and police. [https://www.csoonline.com/article/2127645/data-leak-exposes-personal-data-of-indian-military-and-police.html]
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Data breaches in India. [ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_breaches_in_India]
- Doshi, V. (January 4, 2018). A security breach in India has left a billion people at risk of identity theft. [ https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2018/01/04/a-security-breach-in-india-has-left-a-billion-people-at-risk-of-identity-theft/]
- The Guardian. (January 4, 2018). India national ID database data leak bought online Aadhaar. [ https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/jan/04/india-national-id-database-data-leak-bought-online-aadhaar]
- Sapkale, Y. (February 19, 2019). Aadhaar Data Breach Largest in the World, Says WEF’s Global Risk Report and Avast. [ https://www.moneylife.in/article/aadhaar-data-breach-largest-in-the-world-says-wefs-global-risk-report-and-avast/56384.html]
- The Hindu. (November 7, 2023). How the personal data of 815 million Indians got breached, explained. [ https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/how-the-personal-data-of-815-million-indians-got-breached-explained/article67505760.ece]
- Biometric Update. (n.d.). Indian police adopt facial recognition despite risk of massive data breaches. [ https://www.biometricupdate.com/202405/indian-police-adopt-facial-recognition-despite-risk-of-massive-data-breaches ]
- Cyber Security Concerns for Fintech Companies in India. [ https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cyber-security-concerns-fintech-companies-india-vishwas-thakkar-eyo3f]
- Case Study 1: A Fintech Startup Facing a Data Breach. [ https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cyber-security-concerns-fintech-companies-india-vishwas-thakkar-eyo3f]
- Biggest Cyber Attacks in India. [ https://www.sattrix.com/blog/biggest-cyber-attacks-in-india/]
- Policybazaar Data Breach (2022). [ https://thelegalschool.in/blog/data-privacy-breach-cases-in-india]
- Star Health Insurance Data Leak (2024). [ https://thelegalschool.in/blog/data-privacy-breach-cases-in-india]
- https://fintechnews.sg/110964/fintech-india/cyber-threats-surge-in-indias-financial-sector/
- https://www.biometricupdate.com/202405/indian-police-adopt-facial-recognition-despite-risk-of-massive-data-breaches
- https://idtechwire.com/leak-of-biometric-police-data-in-india-signals-rising-risks/
- Indian police adopt facial recognition despite risk of massive data breaches. [https://www.biometricupdate.com/202405/indian-police-adopt-facial-recognition-despite-risk-of-massive-data-breaches]
- In crime fight, AI cameras give Bengaluru cops a leg-up. [ https://www.deccanherald.com/india/karnataka/bengaluru/in-crime-fight-ai-cameras-give-b-luru-cops-a-leg-up-3212238]
- Hack exposes Indian police facial recognition data amid growing surveillance concerns. [ https://dig.watch/updates/hack-exposes-indian-police-facial-recognition-data-amid-growing-surveillance-concerns]
- Dodgytal: TN Police portal breach highlights need for greater accountability on those storing sensitive personal data. [ https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/toi-editorials/dodgytal-tn-police-portal-breach-highlights-need-for-greater-accountability-on-those-storing-sensitive-personal-data/]
- Leak in Tamil Nadu police’s FRT database. [ https://internetfreedom.in/leak-in-tamil-nadu-polices-frt-database/]
Also Read:
