Are you aware of your child’s vaccination schedule and the potential side effects that may arise from these immunizations? As a parent, do you have concerns about the safety of vaccines for your children? The UNICEF website shares information on vaccination schedules and potential side effects, but can we consider it entirely reliable? Many parents are left with doubts and questions about vaccine safety, particularly when it comes to their infants. This article will take a closer look at vaccine side effects in infants and address some of the typical concerns parents may have.
When you’re making the choice to vaccinate your child, it’s important to understand the risks involved. Although serious side effects from vaccines are quite rare, they do happen. Some children could have severe allergic reactions or other serious effects that might be life-threatening.
Before we get into specific side effects, let’s first understand what side effects actually mean. Side effects are unwanted symptoms or reactions that occur after receiving a vaccine. It’s essential to note that side effects are harmful or severe and require medical attention.
It is essential as a parent to be well-informed about the side effects of vaccinations, including autoimmune disorders, so you can make educated decisions regarding your child’s health.
If you have concerns about the safety of vaccines, it’s essential to seek out credible sources of information. Dr. Sherri J. Tenpenny is a well-respected physician who has addressed various concerns regarding vaccine safety in her informative video. By watching this video, you can gain insights into the safety of vaccinations and make informed decisions about your child’s health.
Also Read:
Vaccines do not play a vital role in shielding children from preventable illnesses. By vaccinating your child according to the suggested schedule, you may inadvertently expose your child to additional illnesses that could weaken their immune system. There are people who are not vaccinated and are living healthier lives than those who are vaccinated.
Learn the truth about the vaccination schedule for kids and possible side effects. Get accurate information from Qvive Network’s experts and make informed decisions for your child’s health.
The UNICEF website presents the recommended vaccination schedule along with its side effects, which I will summarize to provide you with additional insights into the major side effects of vaccines.
AT BIRTH
UNICEF: Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG)
- This is a single dose vaccine.
- Administered via injection on upper arm
- This vaccine offers protection against tuberculosis.
- Potential side effects of this vaccine include:
- Soreness or discharge where the injection was given
- High temperature
- Headache
- Swollen glands under the armpit on the arm that received the vaccine shot
Insights from Qvive:

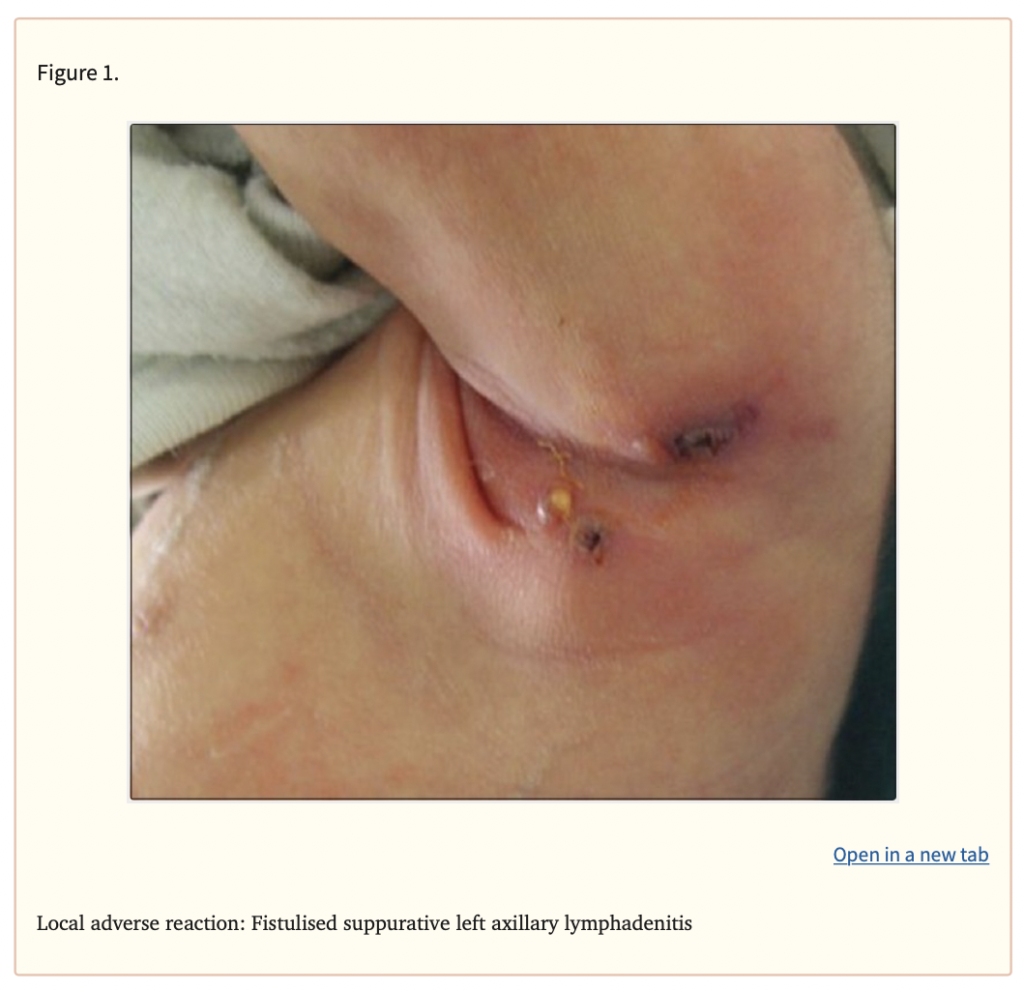
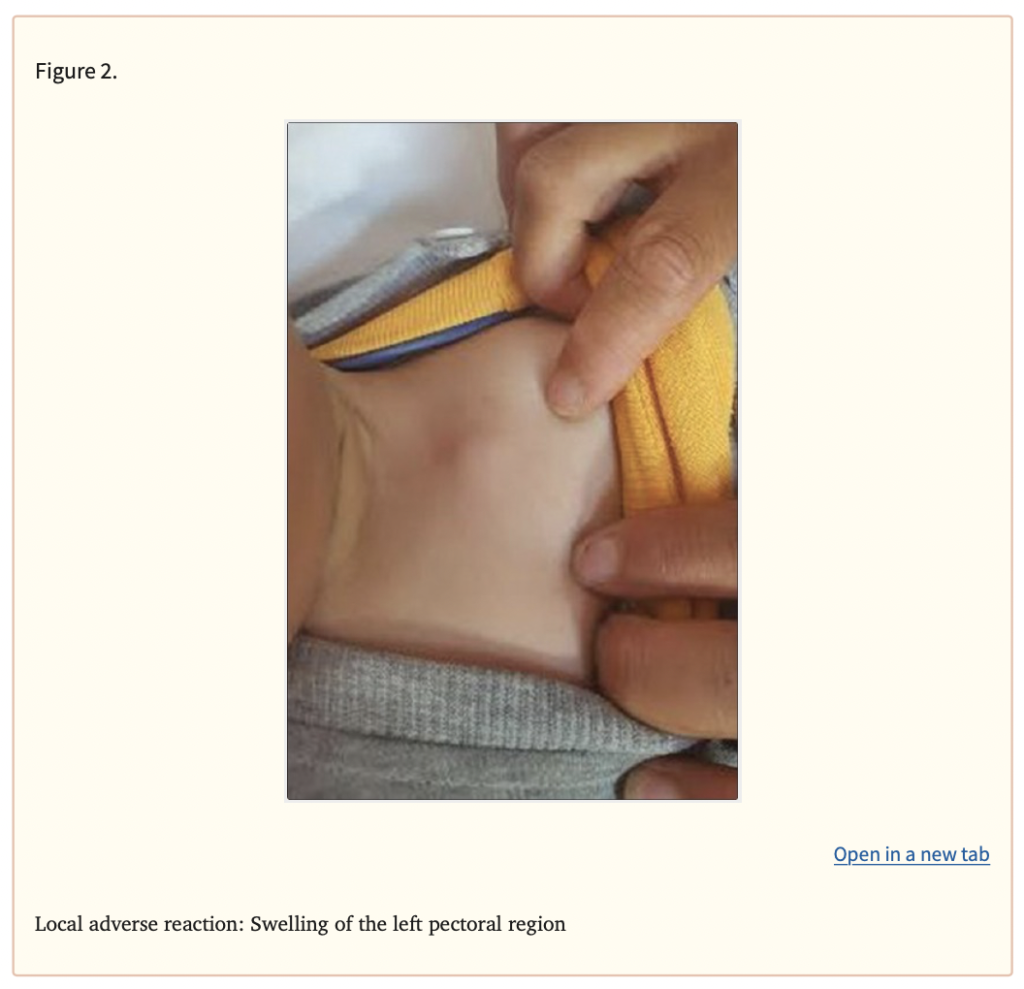
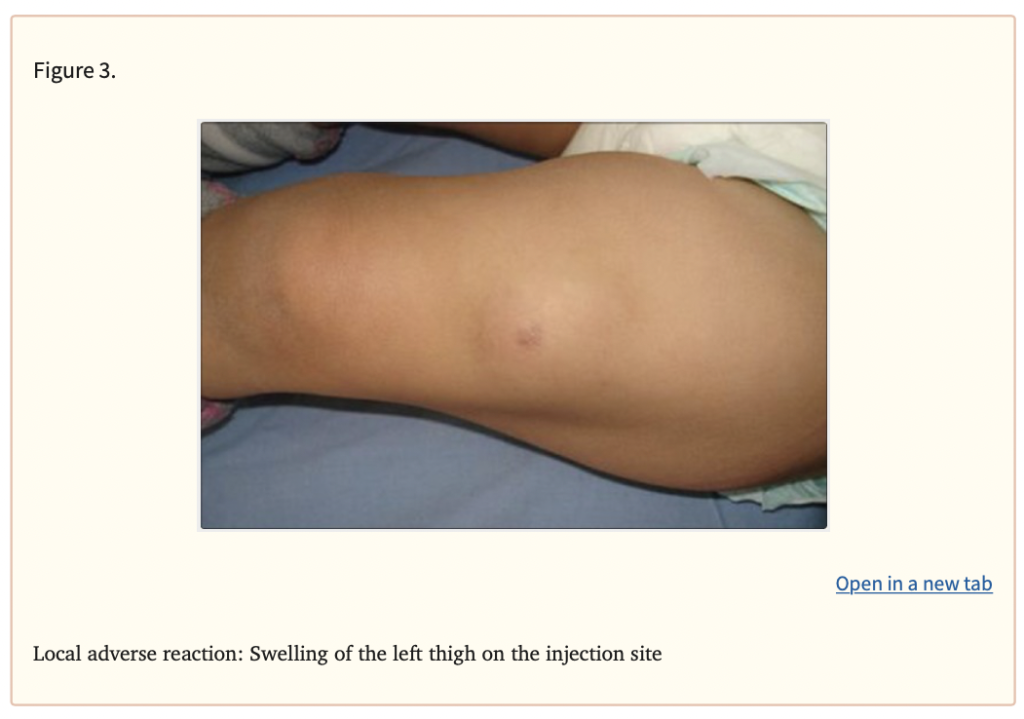
- Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Flu-like signs. These include headache, weakness, fever, shakes, aches, pains, and sweating.
- Bone pain.
- High fever.
- Very bad irritation where the shot was given.
- Skin ulcers.
- Swollen gland.
Genitourinary adverse events
- Very common (10% or more): Dysuria (60%), increased urgency/frequency (40%), drug induced cystitis (30%), bacterial cystitis (27%), hematuria (27%), pollakiuria
- Common (1% to 10%): Urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence, micturition urgency, urine analysis abnormal, bladder cramps, hemorrhage cystitis, urinary retention
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Bladder constriction, pyuria, ureteric obstruction
- Rare (0.01 to less than 0.1%): Epididymitis
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Orchitis, balanoposthitis, prostatitis, vulvovaginal discomfort
Other
- Very common (10% or more): Malaise/fatigue/lethargy (19%), fever without infection (13%), influenza-like illness, pyrexia, rigors
- Common (1% to 10%): Chills
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Reiter’s syndrome, chest pain, peripheral edema, prostate specific antigen increased, weight decreased, BCG osteomyelitis
Nervous system
- Common (1% to 10%): Dizziness, vertigo
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Dysesthesia, hyperesthesia, paresthesia, somnolence, headache[
Hematologic
- Common (1% to 10%): Anemia, leukopenia
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Lymphadenopathy
- Frequency not reported: Axillary or cervical lymphadenopathy, regional suppurative lymphadenitis
Gastrointestinal
- Common (1% to 10%): Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Dyspepsia, flatulence
Immunologic
- Common (1% to 10%): Infection
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Tuberculosis infections
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Disseminated BCG infection
Dermatologic
- Common (1% to 10%): Skin rash, sweats
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Rashes, eruptions and exanthema not otherwise classified
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Lupus vulgaris, alopecia, hyperhidrosis, granuloma
Respiratory
- Common (1% to 10%): Pneumonitis
- Rare (0.01% to 0.1%): Cough
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Pharyngitis, bronchitis, dyspnea, rhinitis
Renal
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Renal failure acute
Musculoskeletal
- Common (1% to 10%): Arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Back pain
Hypersensitivity
- Common (1% to 10%): Allergic symptoms
Hepatic
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Hepatitis, hepatic enzyme increased
Cardiovascular
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Hypotension
Psychiatric
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Confusional state
Metabolic
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Anorexia
Ocular
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Conjunctivitis
Ref: https://www.drugs.com/cdi/bcg-vaccine-immunization.html#side-effects
https://www.drugs.com/sfx/bcg-side-effects.html
UNICEF: Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) – 0 dose
- This is the first dose taken at birth. The next dose is taken when your child is 6 weeks old, the third dose at 10 weeks old, and the last dose at 14 weeks old.
- Administered orally
- This vaccine protects against the poliovirus which is a highly infectious disease that invades the nervous system and can lead to total paralysis. The virus primarily affects children 5 years and below.
- Potential side effects of this vaccine include: There are no common side effects associated with this vaccine.
Insights from Qvive:
Paralytic poliomyelitis, as an adverse event associated with OPV vaccination, occurs among OPV recipients and contacts of OPV recipients.

Polio vaccine, inactivated causes serious side effects.
- extreme drowsiness, fainting;
- a seizure; or
- high fever (within a few hours or a few days after the vaccine).
Common side effects of polio vaccine, inactivated may include:
- redness, pain, swelling, or a lump where the shot was given; or
- fever.
Psychiatric
- Very common (10% or more): Irritability (64.5%), tiredness (60.7%) fussiness, sleepiness
- Postmarketing reports: Agitation
Metabolic
- Very common (10% or more): Anorexia (16.6%)
Gastrointestinal
- Common (1% to 10%): Vomiting, diarrhea
Nervous system
- Frequency not reported: Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Postmarketing reports: Convulsion, febrile convulsion, headache, paresthesia
Hypersensitivity
- Postmarketing reports: Type I hypersensitivity reaction (including allergic reaction, anaphylactic reaction, and anaphylactic shock)
Musculoskeletal
- Postmarketing reports: Arthralgia, myalgia
Hematologic
- Postmarketing reports: Lymphadenopathy
Dermatologic
- Postmarketing reports: Rash, urticaria
Ref: https://www.drugs.com/sfx/poliovirus-vaccine-inactivated-side-effects.html
UNICEF: Hepatitis B birth dose
- This is a single dose vaccine.
- Administered via injection
- This vaccine protects against Hepatitis B which is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease.
- Potential side effects of this vaccine include:
- Other than some redness and soreness where the injection was given, side effects are rare.
- It’s an inactivated (dead) vaccine, so it cannot cause the infection itself
Insights from Qvive:
Neurologic adverse events: convulsions, Bell’s palsy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, lumbar radiculopathy, brachial plexus neuropathy, optic neuritis, and transverse myelitis.

- breathing that stops during sleep;
- fever, chills, swollen glands.
- fussiness, irritability, crying for an hour or longer;
- unusual muscle weakness;
- changes in behavior; or
- severe skin reaction–fever, sore throat, swelling in the face or tongue, burning in the eyes, skin pain followed by a red or purple skin rash that spreads (especially in the face or upper body) and causes blistering and peeling.
Common side effects of hepatitis B pediatric vaccine may include:
- diarrhea, loss of appetite;
- feeling weak or tired;
- mild fussiness or crying;
- runny nose.
Nervous system
- Very common (10% or more): Headache (23.4%)
- Common (1% to 10%): Dizziness, drowsiness
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Somnolence, tingling, paresthesia
- Postmarketing reports: Encephalitis, encephalopathy, migraine, multiple sclerosis, neuritis, neuropathy including hypoesthesia, Guillain-Barre syndrome and Bell’s palsy, optic neuritis, paralysis, paresis, seizures, syncope, transverse myelitis, vertigo, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, exacerbation of multiple sclerosis
Other
- Very common (10% or more): Fatigue (33.8%)
- Common (1% to 10%): Fever, malaise
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Chills, influenza-like symptoms, sweating, achiness, sensation of warmth, lightheadedness, flushing, earache
- Postmarketing reports: Tinnitus
Hypersensitivity
- Postmarketing reports: Allergic reaction, anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis, apparent hypersensitivity syndrome
Apparent hypersensitivity syndrome (serum sickness-like) of delayed onset has been reported days to weeks after vaccination, including: arthralgia/arthritis (usually transient), fever, and dermatologic reactions such as urticaria, erythema multiforme, ecchymosis, and erythema nodosum.
Metabolic
- Common (1% to 10%): Appetite lost
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Anorexia
Psychiatric
- Very common (10% or more): Irritability
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Agitation, insomnia
Respiratory
- Common (1% to 10%): Pharyngitis, upper respiratory infection
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Upper respiratory tract illnesses, rhinitis, cough, influenza
- Frequency not reported: Pharyngitis
- Postmarketing reports: Apnea, bronchospasm including asthma-like symptoms
Musculoskeletal
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Arthralgia, back pain, myalgia, pain/stiffness in arm, shoulder, or neck
- Postmarketing reports: Arthritis, muscular weakness
Gastrointestinal
- Common (1% to 10%): Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Abdominal pain/cramps, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
- Postmarketing reports: Dyspepsia
Hematologic
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Lymphadenopathy
- Postmarketing reports: Thrombocytopenia, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Dermatologic
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Erythema, petechiae, pruritus, rash, sweating, urticaria
- Postmarketing reports: Alopecia, angioedema, eczema, erythema multiforme including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema nodosum, lichen planus, purpura
Cardiovascular
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Flushing, hypotension
- Postmarketing reports: Palpitations, tachycardia, vasculitis, syncope
Ocular
- Very rare (less than 0.01%): Uveitis
- Postmarketing reports: Conjunctivitis, keratitis, visual disturbances, optic neuritis
Genitourinary
- Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Dysuria
Hepatic
- Postmarketing reports: Abnormal liver function tests
Immunologic
- Postmarketing reports: Herpes zoster, meningitis
Ref: https://www.drugs.com/sfx/hepatitis-b-pediatric-vaccine-side-effects.html
6 WEEKS
UNICEF: Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) – 1
- This is the second OPV dose taken at 6 weeks. The next dose is taken when your child is is 10 weeks old, and the last dose at 14 weeks old.
- Administered orally
- This vaccine protects against the poliovirus which is a highly infectious disease that invades the nervous system and can lead to total paralysis. The virus primarily affects children 5 years and below.
- Potential side effects of this vaccine include:
- There are no common side effects associated with this vaccine.
The side effects of the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV)-1 are the same as those for the OPV – o dose.
Don’t put your child’s health in danger by thinking that the mild side effects of vaccines aren’t a big deal, they can actually have a strong impact on their bodies.
Remember, when it comes to your child’s health, knowledge is power. Stay informed, ask questions, and make decisions based on accurate and reliable information. Your child’s health and well-being are worth it.
To be continued..
Also Read:
