Critics Question Timing of Cloud Seeding as Air Pollution Worsens, Citing Possible Data Tampering
A controversial cloud seeding initiative by the Delhi government, intended to curb air pollution, has come under scrutiny after residents and environmental activists claimed that toxic air levels surged following the operation. Additionally, allegations have surfaced that the government may have manipulated Air Quality Index (AQI) data prior to the seeding to justify the project.
Cloud Seeding: A Gamble with Unpredictable Outcomes
Authorities in Delhi-NCR, in collaboration with IIT Kanpur, initiated an ambitious cloud seeding operation on October 28, 2025, in an attempt to combat the city’s hazardous air pollution levels. However, the project has now come under scrutiny, with experts and residents questioning whether the introduction of silver iodide (AgI) into the atmosphere has inadvertently worsened air toxicity.
Silver iodide (AgI), the compound released into the clouds, is under scrutiny for potential health and environmental risks. While it is commonly used in cloud seeding globally, critics argue that its dispersal in an already toxic atmosphere could have dangerous consequences.
Dust Suppressants: A Surface-Level Solution to a Deep-Rooted Problem
The Delhi government employs several dust suppressant powders as part of their air pollution control strategy. These powders contain specific chemical formulations designed to effectively control dust while managing environmental impacts.
Are there any negative side effects or unintended consequences associated with using dust suppression chemicals?
Yes, dust suppression chemicals can have several negative side effects and unintended consequences. These effects span multiple categories and can impact various aspects of the environment and human health.
Environmental Impacts
- Water System Effects
- Contamination of storm drains and waterways
- Impact on aquatic ecosystems
- Disruption of natural water cycles
- Long-term accumulation in water bodies
- Soil Degradation
- Alteration of soil pH levels
- Disruption of nutrient cycles
- Impact on beneficial microorganisms
- Reduced soil permeability
- Air Quality Issues
- Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions
- Particulate matter redistribution
- Chemical vapor formation
- Atmospheric contamination
Health-Related Concerns
- Respiratory Problems
- Chemical mist inhalation
- Irritation of the respiratory tract
- Exacerbation of existing conditions
- Long-term lung damage potential
- Skin and Eye Exposure
- Direct contact irritation
- Chemical burns
- Eye damage
- Dermatitis development
- Systemic Effects
- Chemical absorption through skin
- Systemic toxicity risks
- Organ damage potential
- Neurological impacts
Emerging Technologies
- Smart Dust Control Systems: represent the convergence of IoT, AI, and dust control technology. These systems can predict when and where dust emissions will likely occur and automatically adjust suppression methods accordingly. This predictive approach is far more efficient than traditional reactive methods.
- Nanotechnology: dust control involves using nanoparticles to capture dust particles or change the surface properties of areas prone to dust emission. These technologies promise minimal environmental impact and high efficiency but are still developing.
- Biological solutions: include bioengineering methods and natural dust-binding agents, offering an eco-friendly alternative to chemical suppressants. These methods use biological materials or processes to control dust, potentially reducing the ecological footprint significantly.

Primary Chemical Formulations
- Calcium Chloride-Based Powders
- Highly hygroscopic compounds
- Strong moisture retention properties
- Long-lasting surface protection
- Effective in dry conditions
- Magnesium Chloride Formulations
- Lower corrosion potential
- Environmental benefits
- Similar moisture retention
- Reduced environmental impact
Side Effects and Health Impacts
- Environmental Effects
- Soil pH alteration
- Groundwater contamination risk
- Impact on beneficial microorganisms
- Ecosystem disruption potential
- Health-Related Concerns
- Respiratory irritation
- Skin and eye exposure risks
- Systemic toxicity potential
- Long-term exposure risks
Safety Measures and Guidelines
- Implementation Protocols
- Weather condition monitoring
- Population density assessment
- Application rate restrictions
- Regular monitoring requirements
- Emergency Response
- Spill response guidelines
- Exposure treatment protocols
- System shutdown mechanisms
- First aid station requirements
#WATCH | Delhi: An anti-smog gun being used to spray water to curb air pollution; visuals from Qutub Minar area pic.twitter.com/blWg3MwLnZ
— ANI (@ANI) November 5, 2022
Truck-mounted anti-smog guns
- Number: 200 guns are being hired by the Public Works Department (PWD).
- Function: These are mobile units that spray atomized water to settle dust and other suspended particles in the atmosphere.
- Operation: They will operate in 8-hour daily shifts across all 11 zones under the PWD’s jurisdiction to provide continuous mitigation.

Globally, studies have shown that dust suppressants have limited effectiveness in controlling fine particulate matter (such as PM2.5, which is smaller than 2.5 micrometres) that can be inhaled into the lungs. In November 2019, the Delhi government advised the use of magnesium chloride hexahydrate as a dust suppressant. However, this recommendation is accompanied by serious concerns.
Delhi shrouded in smog as air quality remains in the 'Severe' category; Visuals from the area around Signature Bridge. pic.twitter.com/Ksld9ZSo0N
— ANI (@ANI) November 5, 2022
First and foremost, in cities like Delhi, characterized by a semi-arid climate, the application of water can enhance air moisture, encouraging the spread of micro-organisms. Moreover, dust suppressants can result in increased pollution. For instance, dust suppressants that cling to soil particles can be reintroduced into the air by powerful winds. Additionally, these suppressants may contain volatile organic compounds that are emitted into the atmosphere. This may be detrimental to air quality and facilitate the development of ozone, a pollutant that causes respiratory health issues.
Secondly, municipal employees who apply dust suppressants are at a greater risk of inhaling these chemical substances. When used in urban settings, dust suppressants can also penetrate the skin of individuals nearby. Commuters, rickshaw drivers, street vendors, pedestrians, and especially those from lower socio-economic backgrounds, are at a heightened risk of exposure.
In addition, while magnesium and chlorides are vital nutrients for plant growth, an increase in their levels in the soil can negatively impact plant development. Elevated concentrations of magnesium and chlorides hinder plants’ ability to absorb water and other essential nutrients from the soil. When chlorides build up at the edges of leaves, parts of the leaf may turn yellow or wilt, signaling chloride toxicity.
The recent protests in Delhi and allegations of AQI data manipulation are part of a larger air pollution crisis in the city:
Current Air Quality Crisis
- AQI reached severe levels (414-507)
- Levels are 20-30 times higher than the safe limit
- Air quality has remained in “poor” or “very poor” category since Diwali
Allegations of Data Manipulation
- AAP accuses BJP government of tampering with air quality monitoring stations
- Claims include:
- Shutting down monitoring stations
- Spraying stations to lower readings
- Manipulating data during the worst pollution periods
Protest Details
- Held at India Gate on November 9, 2025
- Approximately 400 participants, including:
- Children and parents
- Environmental activists
- University students
- Journalists
- Demonstrators wore gas masks as a symbolic protest
- Banners displayed messages like “Right to live, not just survive” and “Life in Delhi: Take birth, breathe, die”

Earlier, there were protests against air pollution
2024 | Anand Vihar Chowk (one of the spots) | Bharatiya Janata Party (Delhi unit) Youth Wing | “BJP Youth Wing protests against AAP govt over spike in air pollution”
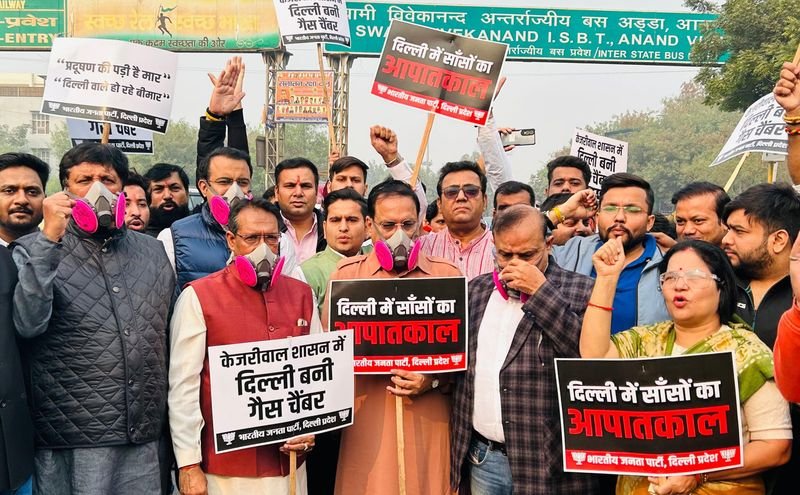


2023 | Multiple points: ITO Crossing, 11 Murti T-point, etc. | Delhi BJP leaders & workers | “Delhi BJP leaders hold protests against AAP govt over air pollution”



* स्वास्थ्य और पर्यावरण विशेषज्ञों का कुछ खास संस्थाओं से ही आना और दूसरे स्वतंत्र विशेषज्ञों को दरकिनार करना।
— Sahil S. Goyal Advocate (@SahilGoyalAdv) November 17, 2022
* यूनाइटेड नेशन और गेट्स फाउंडेशन का हमारी सरकारी तंत्र में दखल होना।
कुछ बातों पे थोड़ी तीखी नोक झोंक भी हुई।#ClimateScam #ClimateChange #oldcarban #nwo #UnitedNations pic.twitter.com/OxWDyixi4K
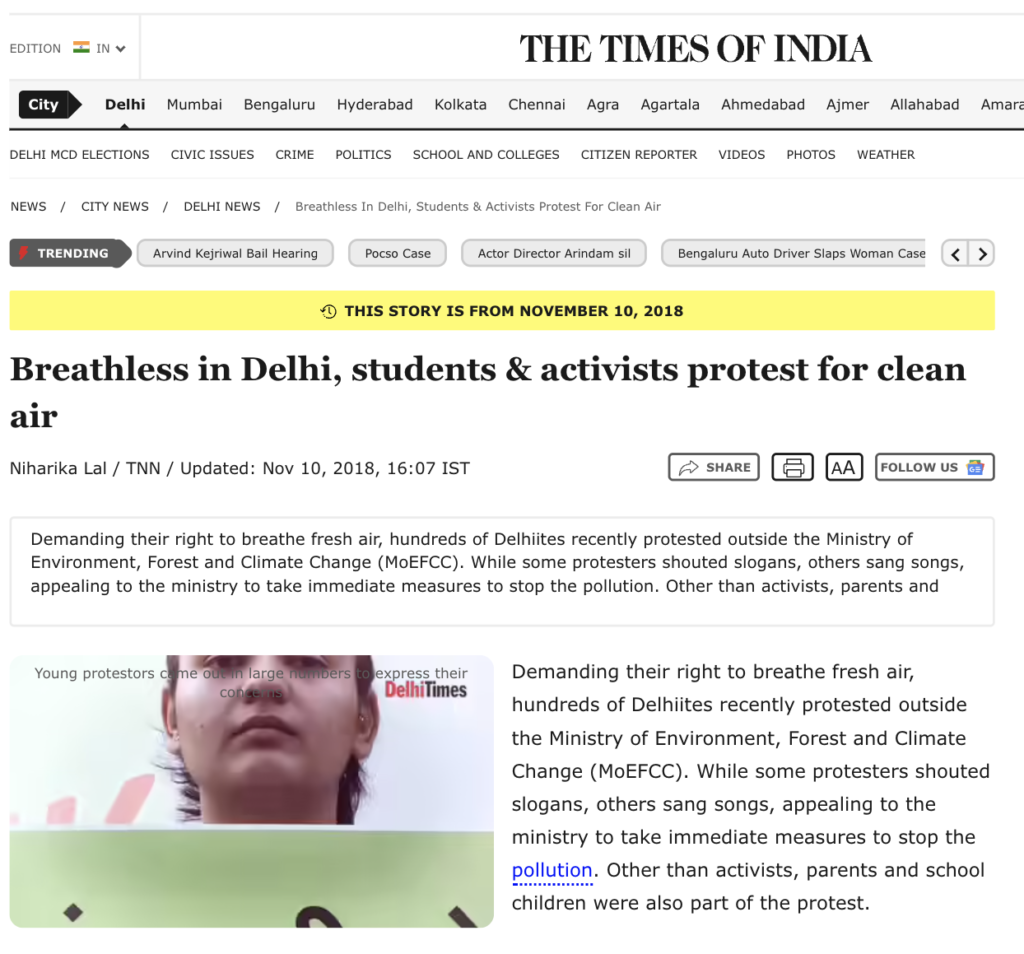
2018 | Near Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEFCC) or central Delhi zone | Students & activists | “Breathless in Delhi, students & activists protest for clean air”
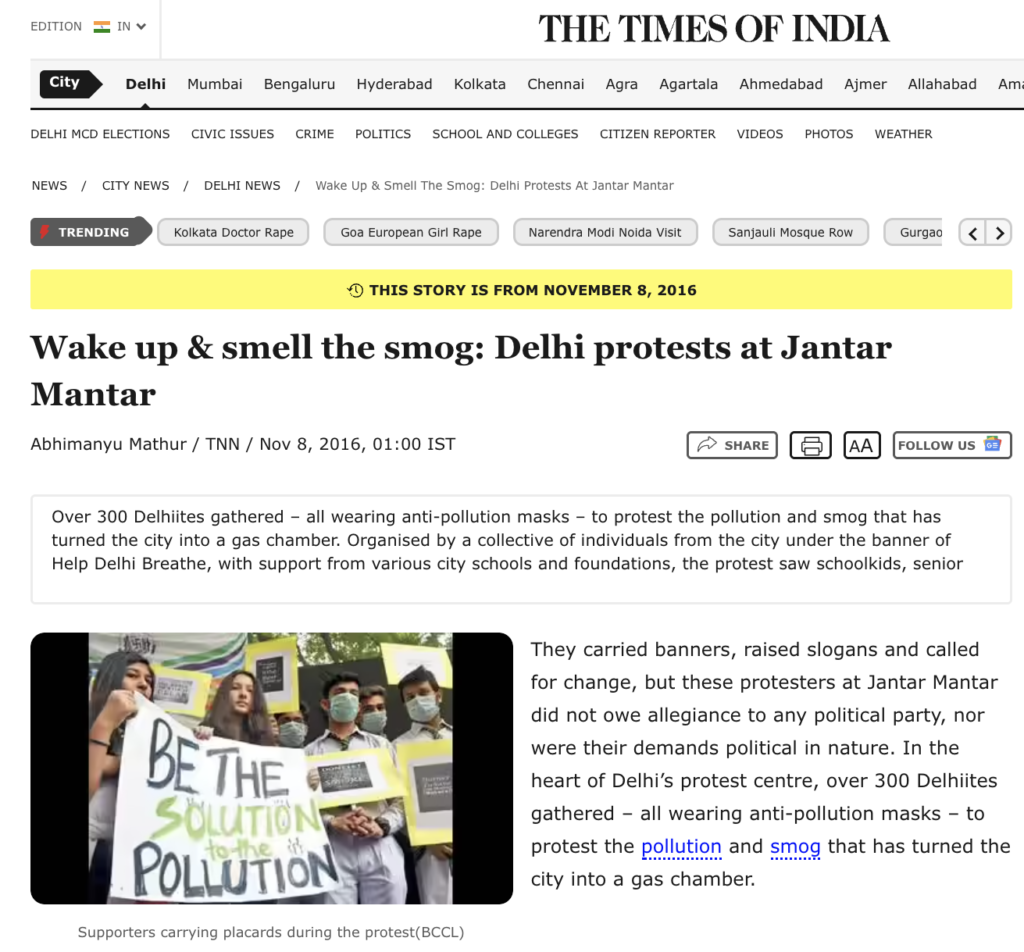
2016 | Jantar Mantar, Delhi | Collective of individuals (“Help Delhi Breathe”) & schools/foundations | “Wake up & smell the smog: Delhi protests at Jantar Mantar”
Government actions to combat so-called air pollution in Delhi have evolved significantly over three decades. Here’s a comprehensive timeline:
Early Actions (1990s)
| YEAR | ACTION | DETAILS |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | First Action Plan | The Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority was established for the NCR region |
| 1998 | EPCA Formation | Implementation began for converting vehicles to compressed natural gas (CNG), including the entire city bus fleet |
| 1998 | Vehicle Conversion | The Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority was established for NCR region |
Second Wave (2010-2015)
| YEAR | ACTION | DETAILS |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | BSIV Standards | Implemented BSIV emission standards for vehicles in Delhi and metropolitan cities |
| 2014 | Air Quality Index | The National Air Quality Index (NAQI) was created for transparency and public awareness |
Major Interventions (2015-Present)
| YEAR | ACTION | DETAILS |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Supreme Court Orders | Significant judicial interventions regarding public transport, clean fuels, and vehicular emissions |
| 2016 | Great Smog Response | The Supreme Court banned firecracker sales in Delhi |
| 2017 | Firecracker Ban | Permanent shutdown of a major polluting facility |
| 2018 | Badarpur Power Plant | Establishment of a 10-member air pollution control team |
| 2020 | Control Team Formation | Declared a Health Emergency during a severe pollution crisis |
| 2021 | Emergency Measures | The Supreme Court advised the Punjab Government on agricultural practices |
| 2023 | Stubble Burning Action | Supreme Court advised the Punjab Government on agricultural practices |
| 2025 | Vehicle Restrictions | The Supreme Court advised the Punjab Government on agricultural practices |
Should the World Health Organization and Bill Gates be in charge of tackling air pollution? It’s a big question. And what about the apps popping up in India? A lot is going on with programs aimed at addressing air quality. But who exactly is responsible for keeping our air clean?
In a shocking revelation, the US military conducted secret biological warfare experiments on its own citizens without their knowledge. This operation, known as Operation Sea Spray, transformed the bustling city into an unwitting laboratory for testing disease dispersion.
Ref:
- https://www.nationalheraldindia.com/national/delhi-aqi-severe-for-second-day-in-a-row-minimum-temperature-drops-to-104-degrees
- https://m.economictimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/govts-intention-is-not-to-reduce-pollution-but-to-reduce-its-figures-aap-slams-bjp/articleshow/125212641.cms
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/others/htinterviewdelhi-aqi-data-fully-transparent-can-t-be-fudged-says-sirsa-101762885007229-amp.html
- https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c1k02lregw0o
- https://www.downtoearth.org.in/air/fighting-air-pollution-in-delhi-for-2-decades-a-short-but-lethal-history-67585
- https://oizom.com/dust-suppression-solutions/
- https://scroll.in/article/1041131/anti-smog-guns-sprinklers-dust-suppressants-how-effective-are-these-quick-fixes-to-air-pollution
- Youtube
Also Read:
