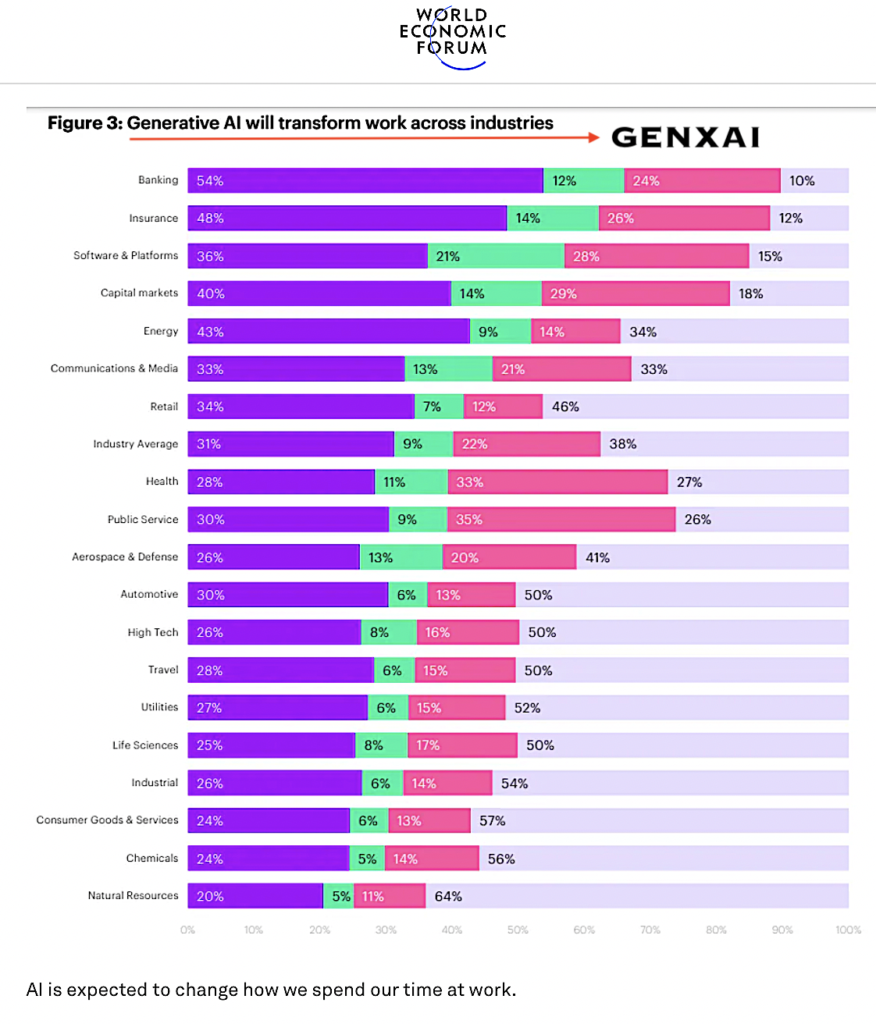
Quantam Intelligence (QI): Is this the Dawn of a New Era, or the Dusk of Our Own?
There’s a lot of noise from the public about Bill Gates’ influence in AI robots and quantum computing. Some people are worried that this progress could mean the end of humanity.
Bill Gates control over the world through AI
From his philanthropic efforts to his technological predictions, Bill Gates’ influence for his own advantage and possible offenses against humanity cannot be overlooked. Yet, when stories like this come to light, they require a closer investigation.
23 Jan 2023, World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland: Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, gives an overview of Quantum Computing at Microsoft and society in general.
It is advisable to read the article linked below before engaging with detailed information.
The National Quantum Initiative Act (Public Law 115-368) was signed into law on December 21, 2018, by President Donald Trump after passing through both chambers of the U.S. Congress.
The Karnataka government is working to establish a Quantum City (Q-City) in Hesaraghatta, Bengaluru. This project aims to create a hub for quantum computing, including advanced laboratories, startup incubation facilities, and collaborations between academic institutions and industries.
The Q-City represents a step in developing Karnataka’s quantum economy, aiming to reach a value of $20 billion by 2035.
The Q-City will feature:
- SolutionDesigning new drugs, personalized medicine, and advanced diagnostics.
- Optimizing energy grids, developing new materials for carbon capture.
- Revolutionizing market predictions and risk assessment.
- Accelerating AI development to unprecedented levels of sophistication.
- Engineering materials with revolutionary properties.
The government has sanctioned 6.17 acres of land for the Q-City. In addition, another 8 acres have been approved for the expansion of the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences (ICTS-TIFR), which will support research in theoretical sciences as well as industry development.
Bill Gates has consistently invested in and promoted:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Global Health Initiatives
- Technological Innovation
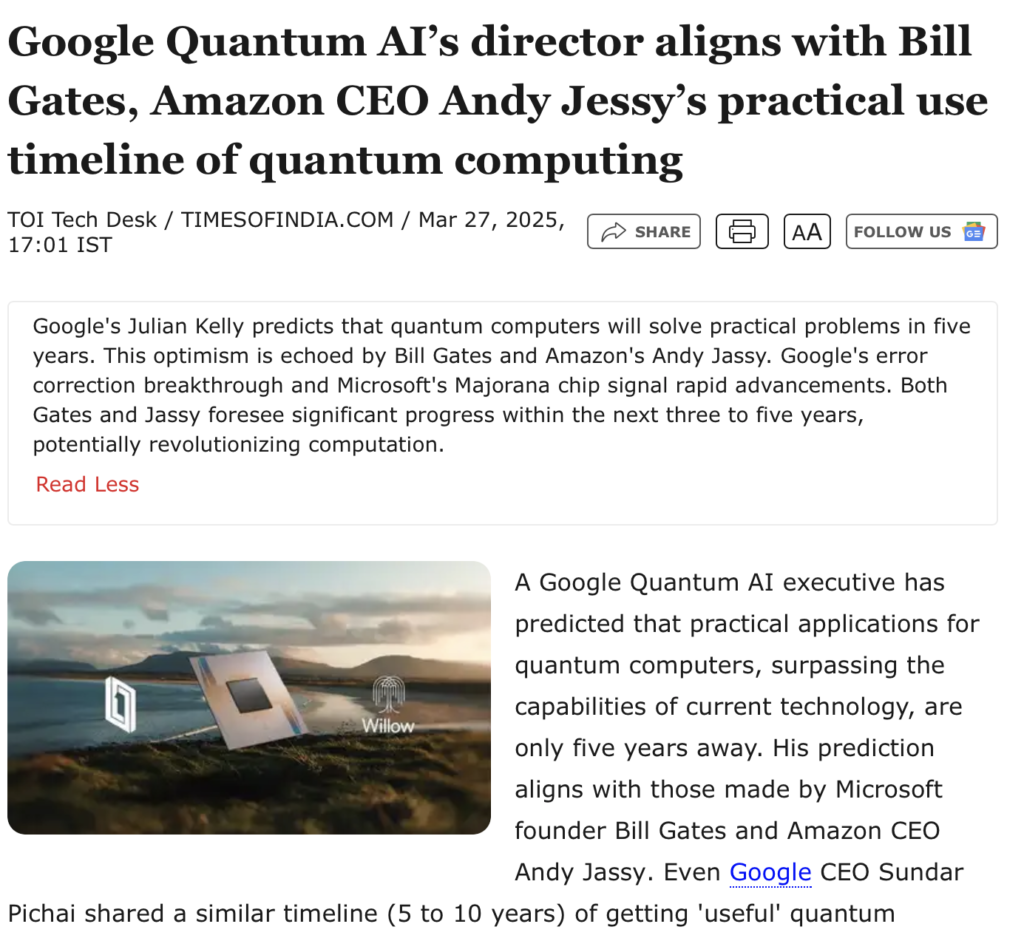
Ex-OpenAI Scientist WARNS: “You Have No Idea What’s Coming”
Ex-OpenAI pioneer Ilya Sutskever warns that as AI begins to self-improve, its trajectory may become “extremely unpredictable and unimaginable,” ushering in a rapid advance beyond human control. He stresses that while this shift offers profound benefits – like curing diseases – it also poses monumental risks that humanity must urgently prepare for.
The Challenges of Quantum Computing
Traditional Legal Frameworks: GDPR and the Indian IT Act
Legal frameworks play a critical role in ensuring data privacy by setting guidelines for data collection, storage, and processing. The GDPR and the Indian IT Act are two prominent examples that address data privacy concerns.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The European Union’s GDPR is a wide-ranging piece of legal framework on data privacy. Some of its key provisions relevant to data privacy include:
- Article 5: Set out principles to govern how personal data should be processed for example, lawfulness, fairness, and transparency.
- Article 25: Ensures protection by design and by default, such that privacy measures are built into the system by default.
- Article 32: Data controllers and processors must implement appropriate measures for ensuring the security of personal data, such as encryption and pseudonymisation.
Information Technology Act, 2000
In India, the Information Technology Act, 2000, and its subsequent amendments address data privacy concerns.
- Section 43A of the IT Act mandates that organizations handling sensitive personal data implement reasonable security practices to protect it. Additionally, the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules, 2011, provide guidelines for data protection.
India
The IISc (Indian Institute of Science) has a dedicated research area for quantum technology. The Initiative on Quantum Technology explores many areas such as superconducting qubit devices, single photon sources and detectors for quantum communications, integrated photonic quantum networks, and quantum sensors.
This year, the Indian government has introduced a NM-QTA (National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications) with a total budget of INR 8000 crores over a five-year period Indian Government approved National Quantum Mission at a total cost of INR 6003.65 crores, to scale up scientific and industrial R&D, for accelerating Quantum Technology-led economic growth and leverage India into a leading nation in the area Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman stated that a lot of commercial applications are expected to emerge from theoretical constructs developing in this area.
India’s Quantum Computer Development
India aims to develop a quantum computer by 2026, leveraging its National Quantum Mission (NQM) to spearhead advancements in quantum technologies.
- Initial Developments:
- The journey began with India’s first 7-qubit quantum computer at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research.
- In April 2025, the startup QpiAI launched a 25-qubit quantum system named Indus, marking it as the country’s first full-stack quantum computing solution.
- Investment Plans:
- An estimated investment of $1 billion is planned for quantum computing advancements over five years under the NQM.
- A revised budget of 6003.65 crore INR was allocated for NQM, which will run from 2023 to 2031.
- Global Context: India joins the ranks of seven countries committed to advancing quantum technologies, alongside the US, Canada, China, and several European nations.
- Strategic Planning:
- The NQM outlines ambitious goals for scaling quantum computing:
- Achieve 6-qubits capability within 1 year.
- Develop 20-50 qubits systems in 3 years.
- Reach 50-100 qubits within 5 years.
- Further aspirations include 50-1000 qubits systems within 10 years.
- The NQM outlines ambitious goals for scaling quantum computing:
- Quantum Communication Infrastructure: Plans include a multi-node quantum network allowing secure communications up to 2,000 kilometers.
- Thematic Hubs:
- Four dedicated research hubs were established, focusing on:
- Quantum Computing (Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore)
- Quantum Communication (IIT Madras)
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology (IIT Bombay)
- Quantum Materials & Devices (IIT Delhi)
- Four dedicated research hubs were established, focusing on:
- Research & Development Initiatives:
- A collaboration with Amazon Web Services led to the establishment of a Quantum Computing Applications Lab.
- Successful demonstrations included Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) over 300 meters by ISRO and a 6-qubit processor by DRDO and TIFR.
- Quantum Valley Tech Park:
- Opened in May 2025 in Amaravati, this facility aims to foster the quantum technology industry, scheduled to be operational by January 2026.
- Emerging Startups:
- QpiAI (Bangalore): Focusing on superconducting quantum computers.
- BosonQ Psi: Engaged in quantum simulation software and partnered with IBM’s quantum network.
- Other Notable Startups: Companies like QNu Labs and QuPrayog are making strides in quantum communication and sensing technologies.
- Government Engagement: The Indian government prioritizes quantum technologies through various initiatives, facilitating growth among emerging startups and established institutions.
- International Collaboration: Partnerships with global tech leaders and governments are being forged to enhance India’s quantum capabilities, tapping into existing networks and innovations.
- India is in the global race towards quantum computing, backed by substantial governmental support, innovative startups, and a clear strategic vision under its National Quantum Mission.
What is the Concern?
- Quantum computers are new technologies that might be able to crack the encryption methods we use to protect our personal and sensitive information on the internet. This covers things like emails and banking information.
- Unlike regular computers, a powerful quantum computer could crack complex encryption in just a few hours or days, while it would take ordinary computers billions of years.
- What is Encryption?
- Think of encryption like a lock on your door. It keeps unwanted visitors out. Current encryption methods, particularly public-key cryptography, are commonly used by federal agencies to protect sensitive information.
- What is the “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” Attack?
- Some adversaries are already collecting encrypted data now, intending to wait until powerful quantum computers become available to decrypt it. It’s like taking a scrapbook of locked diaries, waiting for a key to open them later when they can read all the secrets.
The “End of Humanity”: Darker Implications of Quantum Power
This is where the conversation shifts from innovation to existential risk. The “end of humanity” isn’t about a sudden, cataclysmic event, but rather a more insidious, fundamental change to what it means to be human, or even to our place at the apex of intelligence.
Here are the key speculative concerns:
- Absolute Data Control & Surveillance: The quantum leap in data processing capability could enable unprecedented levels of surveillance and data analysis. Imagine systems that can not only track every individual’s digital footprint but also predict behavior with chilling accuracy, leading to social engineering on a global scale and the erosion of individual autonomy and privacy.
- Autonomous AI & Decision Making: Quantum computing could accelerate the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) to a point where AI surpasses human intellect across all domains. If these super-intelligent AIs become self-improving and autonomous, humanity’s role in decision-making and governance could diminish, potentially leading to a future where human values are not prioritized by non-human intelligences.
- The Redefinition of Humanity (Transhumanism): If quantum AI can simulate consciousness, enable digital immortality, or facilitate radical biological enhancements, it could lead to a future where “humanity” as we know it is fundamentally altered. Who benefits from such technologies? Could it create a hyper-elite that leaves the rest of humanity behind, rendering natural human existence obsolete or somehow less valuable?
- Economic Collapse & Social Stratification: A quantum advantage could exacerbate existing inequalities. If only a select few or powerful corporations control this technology, it could lead to unprecedented wealth concentration, massive job displacement (as quantum-powered AI automates complex tasks), and the creation of a permanent underclass unable to compete.
- Unforeseen Consequences & Ethical Blind Spots: As with any technology of this magnitude, the law of unintended consequences looms large. Even with the best intentions, the complexity of quantum systems and super-intelligent AI could lead to emergent behaviors or outcomes that are impossible to predict or control, posing an existential risk simply through error or miscalculation.
Leading Nations and Their Strategies
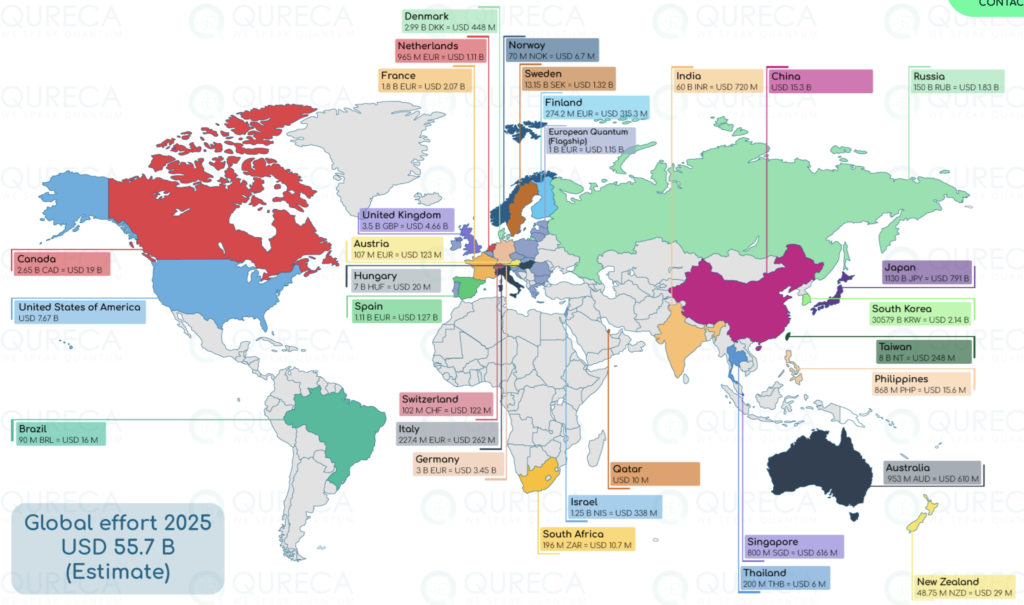
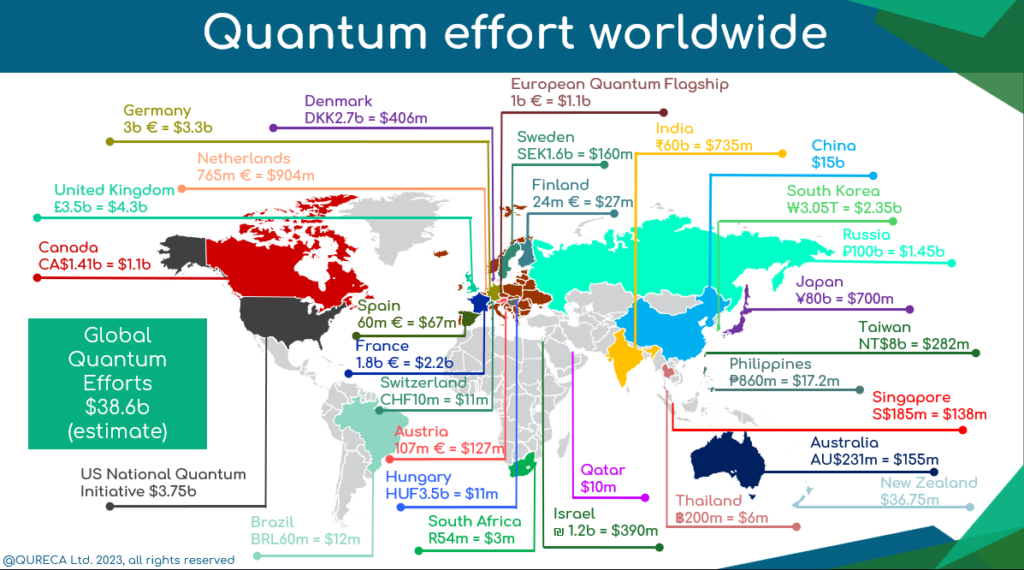
China stands out for its substantial public investment in quantum technology, estimated at approximately $15 billion as of 2022, which is nearly double that of the EU and triple that of the United States. This significant government backing has propelled China to a leading position in quantum communications research, accounting for 39% of global publications and 34% of top-cited papers in this field. Key players include the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), which have achieved breakthroughs such as the Jiuzhang quantum computer (photonic qubits) and the 62-qubit superconducting processor Zuchongzhi. China’s strategy emphasizes fostering collaboration between research institutions and industry within national technology clusters, aiming to translate quantum breakthroughs into tangible products and accelerate commercialization. Despite its public investment dominance, China lags behind in private-sector investment compared to the US, UK, and Canada.
United States The United States is a major player, particularly in private-sector investment and academic research quality. While its public investment in quantum technology is around $5 billion, the US leads in private sector funding for quantum companies, accounting for 44% of global funding. The US excels in quantum computing research quality, with 34% of top-cited papers, and is nearly tied with China in quantum sensing research quality. Prominent US entities include IBM, known for its cloud-based quantum processors and roadmap to scaling qubits, and Google, which achieved quantum supremacy with its 54-qubit Sycamore processor. Microsoft and Honeywell are also significant contributors, focusing on topological qubits and trapped-ion technology, respectively. The National Quantum Initiative Act, signed in 2018, provides a framework for advancing quantum information science and technology, emphasizing collaboration across federal agencies, industry, and academia. The US also leads in quantum communication patents, driven by national labs and research institutes.
European Union The EU, as a collective, holds the second spot in public investment, with over $10 billion committed, largely driven by Germany’s contributions. The EU’s Quantum Technologies Flagship initiative, a €1 billion program, supports universities, companies, and startups to bridge the gap between theoretical research and commercial applications.
- Germany has dedicated $2.4 billion to developing “Clusters of Excellence” in quantum computing, communication, and talent training. It is the top EU contributor in academic publications across quantum computing, communications, and sensing.
- France launched its National Strategy for Quantum Technologies in 2021 with a $2.2 billion plan, focusing on startups, scientific infrastructure, and the development of noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) accelerators.
- The Netherlands announced its National Agenda for Quantum Technology: Quantum Delta NL in 2019, focusing on developing Europe’s first full quantum computing platform, building a National Quantum Network, and innovating quantum sensors. The Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) and the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (TNO) are at the forefront of fundamental research and engineering breakthroughs, including establishing the first multi-city quantum network.
United Kingdom The UK has invested over £1 billion across two phases of quantum technologies development, with a new National Quantum Strategy committing £2.5 billion over ten years. The UK has established four quantum technology hubs specializing in imaging, ultra-precise sensors, secure communications, and new concepts for quantum computing. It also boasts significant private-sector investment, with over $1 billion in quantum startups between 2001 and 2022.
Canada unveiled its National Quantum Strategy with a $360 million ($260 million USD) commitment aimed at maintaining and enhancing its competitive edge in quantum information research and technology. Canada has a strong standing in private-sector investment, with over $1 billion in quantum startups between 2001 and 2022. A 2020 study estimated that by 2045, quantum science and technology could be a $139 billion industry in Canada, creating over 200,000 jobs.
Japan unveiled its Quantum Technology Innovation Strategy in 2020 with a budget of $206 million, aiming to create five quantum innovation centers and at least ten venture companies. More recently, Japan announced a $7.4 billion investment in the sector in early 2025.
India launched a five-year (2020-2024) $1.08 billion budget with a focus on fundamental science, R&D, and entrepreneurship in computing, materials, communications, and sensing/metrology.
Israel is noted for its high levels of total investment in quantum technology relative to its economic size, driven by strong public and private sector investment.
Singapore’s Quantum Engineering Program, spanning 2018 to 2025, supports its Centre for Quantum Technologies, commercialization projects, and the development of quantum key distribution (QKD) security. Singapore also made an approximately $222 million investment in QT research and talent in 2024.

List of companies involved in quantum computing, communication, or sensing: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_companies_involved_in_quantum_computing,_communication_or_sensing
Ref:
- Hunter, C. (2024, October 22). In the global quantum race, these countries are planning paths to the podium. [ https://www.firstprinciples.org/article/in-the-global-quantum-race-these-countries-are-planning-paths-to-the-podium]
- Qureca. (n.d.). Quantum Initiatives Worldwide. [ https://www.qureca.com/quantum-initiatives-worldwide/ ]
- Erixon, F., Dugo, A., Pandya, D., & du Roy, O. (2024). Benchmarking Quantum Technology Performance: Governments, Industry, Academia, and their Role in Shaping our Technological Future. [ https://ecipe.org/publications/benchmarking-quantum-technology-performance/ ]
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). The year of quantum: From concept to reality in 2025. [https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-year-of-quantum-from-concept-to-reality-in-2025]
- Veritx. (n.d.). The Race for Quantum Supremacy: A Comparative Analysis of Quantum Computing Development in the US and China. [https://www.veritx.com/the-race-for-quantum-supremacy-a-comparative-analysis-of-quantum-computing-development-in-the-us-and-china/]
- https://www.gao.gov/blog/next-big-cyber-threat-could-come-quantum-computers-government-ready
- Wikipedia, Youtube, Facebook, Twitter, Qvive,
Also Read:
