Did you know that electronic waste, also known as e-waste, is one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world? With the rapid advancement of technology, more and more electronic devices are being produced, leading to a staggering amount of e-waste being generated each year. This has significant implications for the environment and human health, as e-waste contains a multitude of components with valuable materials, some of which are toxic and can have harmful effects

E-waste disposal is a global issue, causing health issues due to air and water pollution
• E-waste is a growing issue globally, containing valuable and toxic materials.
• Countries like China, India, and Africa face recurring e-waste dumping issues.
• The US dumps tons of electronic waste annually, mainly to Guiyu, China.
• Poor e-waste management harms the population and environment.
• Technological advancements lead to more old electronics being discarded and exported to developing countries.
• Lack of proper disposal and recycling facilities and procedures is a significant challenge.
• E-waste is generated through recycling and dumping from other countries.
• The increasing use of electronic gadgets poses health risks, making disposal and recycling a health nightmare.
Laboratories generate hazardous waste for research and experimentation
Research and development (R&D) laboratories also generate a significant amount of e-waste. As these labs work on creating new products and technologies, they often produce prototypes, experimental devices, and other electronic equipment that may become obsolete or no longer needed.
It is important for R&D laboratories to be aware of the environmental impact of their activities and to implement sustainable practices for managing e-waste. This includes properly recycling and disposing of electronic devices, as well as seeking out ways to reduce waste generation through more efficient design and manufacturing processes.
Pharma industries and vaccine manufacturers activities also have a significant impact on the environment, contributing to climate change and releasing toxic substances that can harm human health and ecosystems.
Vaccine production involves the use of various chemicals and materials that can be harmful to human health and the environment if not properly managed. For example, some vaccines contain preservatives like thimerosal, which is a mercury-based compound that can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life. Additionally, the production of vaccines can generate hazardous waste that needs to be disposed of safely to prevent environmental pollution.
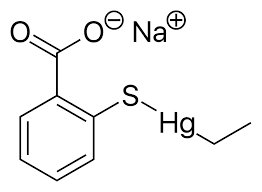
The presence of toxic substances in pharmaceutical products and vaccines can pose serious health risks to individuals who are exposed to them. For instance, long-term exposure to certain preservatives and chemicals used in drug manufacturing can lead to respiratory problems, skin irritation, and other health issues. Moreover, the release of pharmaceutical pollutants into the environment can contaminate food and water sources, potentially causing widespread health problems in communities.
Health Risks: Pharmaceuticals containing toxic substances can lead to adverse health effects, such as allergic reactions, skin irritation, and respiratory issues. Improper disposal of these medications can also result in the contamination of water sources, putting human health at risk.
Environmental Impact: The manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical products can release harmful chemicals and pollutants into the air, water, and soil. These pollutants can disrupt ecosystems, harm wildlife, and contaminate food sources. Additionally, the improper disposal of pharmaceutical waste can further contribute to environmental degradation.
This article will delve into the complexities of e-waste, the impact it has on human health and the environment, and the steps that can be taken to address this pressing issue.
Electronic Waste An Emerging Problem in Countries
In today’s digital age, electronic waste, or e-waste, has become a significant issue in both developed and developing countries across the globe. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, more and more electronic devices are being discarded, leading to a growing problem of electronic waste pollution.
Electronic waste refers to any discarded electronic or electrical devices, including computers, smartphones, tablets, televisions, microwave ovens, and household appliances. They contain hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can pose serious risks to human health and the environment if not properly managed.
The Image (a), (b), (c) and (d) shows how poor people, women and children are used in the E-waste recycling units in India.

When electronic devices end up in landfills or are improperly recycled, toxic substances can leach into the soil and water, contaminating the surrounding environment. This can have detrimental effects on both human health and wildlife, leading to respiratory problems, neurological disorders, and even cancer. In developing countries where e-waste recycling is often informal and unregulated, workers are particularly at risk of exposure to hazardous materials.
In addition to the health risks associated with e-waste, there are also significant environmental consequences. The improper disposal of electronic devices contributes to air and water pollution, soil degradation, and the depletion of natural resources. E-waste recycling processes that are not environmentally friendly can release harmful chemicals into the air, further exacerbating the problem of pollution.
Electronic products are a complex mixture of several hundred tiny components, many of which contain deadly chemicals. These chemicals are a strain on human health and the environment. Most of the components in electronic devices contain lead, cadmium, mercury, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), brominated flame retardants (BFRs), chromium, beryllium etc., TVs, video and computer monitors use CRTs, which have significant amounts of lead and the long term exposure to these substances can damage the nervous system, kidney and bones and the reproductive and endocrine systems and some of them are carcinogenic. These e-wastes will have long lasting effects on the environment, when improperly disposed (incinerated/land filled instead of recycling) with domestic waste, without any controls, can contaminate the soil, water and air. EEEs are made of a multitude of components, some containing toxic substances that have an adverse impact on human health and the environment if not handled properly. Often, these hazards arise due to the improper recycling and disposal processes used. It can have serious repercussions for those in proximity to places where e-waste is recycled or burnt.
Toxic Substances Leaching into the Environment: When electronic waste is improperly disposed of in landfills, the toxic substances within these devices can leach into the soil and groundwater. This contamination can have far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and biodiversity, leading to long-term environmental damage.
Resource Depletion: The extraction of raw materials for the production of electronic devices contributes to deforestation, habitat destruction, and loss of biodiversity. Overall electronic waste leads to increased energy consumption and carbon emissions.
The environmental impact of pharma industries and vaccine manufacturers cannot be ignored. Government officials, prioritize addressing the environmental and health implications of pharma industries and vaccine manufacturing. Let’s focus on real solutions, not distractions.
Source: Wikipedia-Image, Linkedin-Image
Also Read:
