India is increasingly being viewed as a critical proving ground for electric vehicle (EV) adoption by Bill Gates, who sees the nation as a vital “experimental model” for global climate action. Gates has actively advocated for EVs in India, highlighting their potential to combat severe air pollution and reduce carbon emissions. Also, there are lingering questions and doubts about the accuracy and reliability of air quality data in the country. This uncertainty has raised concerns about the effectiveness of EVs in addressing India’s pressing environmental issues.
Why India?
India as a “Model”: Innovation, Experimentation, or Both?
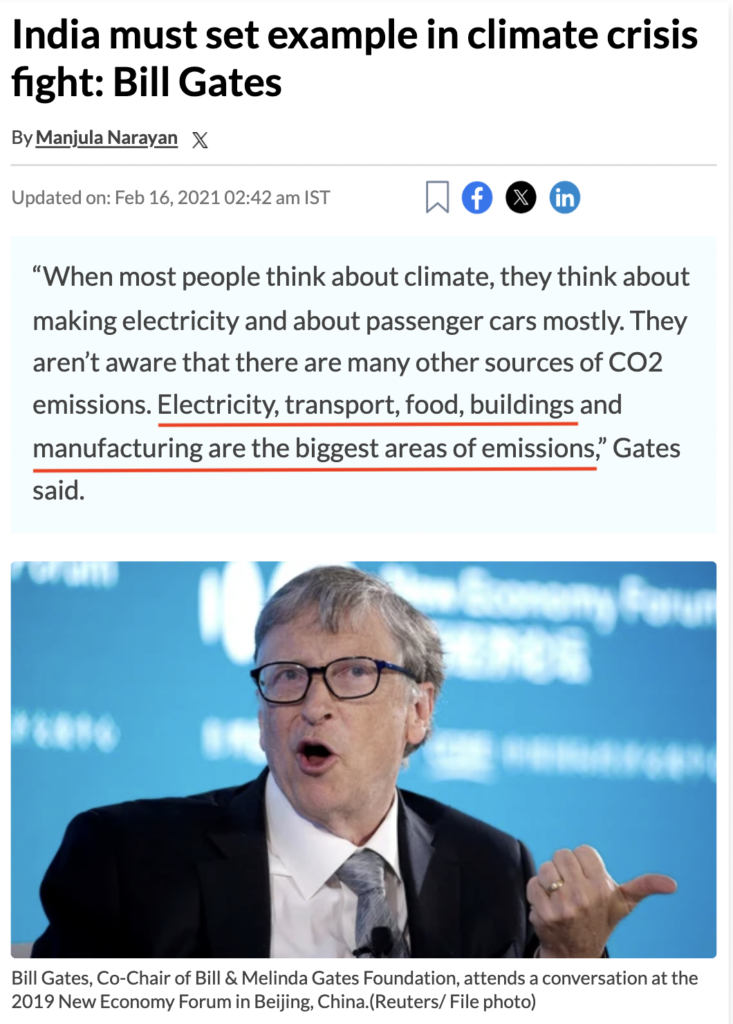
Gates stresses that while electricity generation and passenger cars are often the primary focus when discussing climate change, there are numerous other sources of CO2 emissions, including transportation, food production, buildings, and manufacturing. He believes that India, despite not being the first to reduce emissions, can inspire richer countries to fulfil their climate commitments.
He advocates for the development of alternative fuels, such as advanced biofuels and electrofuels, which can work with existing engines.
Beyond technological advancements, Gates stresses the importance of individual actions and public-private partnerships. He believes that individual choices to adopt sustainable practices can create market signals that encourage governments and businesses to invest in green innovations. He has commended India’s leadership in initiatives like the ‘Lifestyle for the Environment (LiFE) Movement,’ which promotes pro-climate behaviors among citizens.

Furthermore, Gates points out that India faces severe air pollution in its cities, partly due to coal-fired power plants and traditional vehicles. He believes that transitioning to electric vehicles and moving away from coal for power generation would significantly improve air quality and public health. According to the WEF Agenda 2030, he is pushing the indian government to implement more environmental regulations to address these issues.

13 Nov 2025: The Gates Foundation and over 35 other philanthropies in the Climate and Health Funders Coalition have committed an initial $300 million to address the health impacts of climate change.
Funding focus: The funds will support the development of solutions for:
Extreme heat
Air pollution
Climate-sensitive infectious diseases
Strategic goals:
Strengthen health systems
Integrate climate and health data
Protect lives and livelihoods
This initiative, announced at COP30 in Brazil, also supports the Belém Health Action Plan.

MAIN OBJECTIVE
Strengthen the health sector’s adaptation and resilience to climate change by advancing integrated surveillance and monitoring systems, accelerating capacity-building, promoting evidence-based policy implementation, and fostering innovation and sustainable production. This Plan takes into account the diverse needs and national contexts of health systems worldwide, and recognizes the importance of cross-sector collaboration to accelerate mitigation efforts that generate health co-benefits.
GLOBAL TARGET OF THE PLAN
The global objective of this Plan is to integrate the BHAP into UNFCCC progress reporting under the Global Stocktake and other relevant mechanisms. By COP33 (2028), during the next Global Stocktake, all Endorsing Parties will be invited to report on their progress in implementing the actions outlined in the Belém Health Action Plan, aligned with the GGA indicators and any other nationally appropriate indicators.
- Cross-Cutting Principles
- Health Equity and Climate Justice: Focus on reducing health disparities exacerbated by climate change.
- Leadership and Governance: Ensure that adaptation policies prioritize transparency, accountability, and include input from affected communities.
- Action Lines and Measures
- 1. Surveillance and Monitoring
- Establish integrated, participatory climate-informed health surveillance systems.
- Enhance data infrastructure for effective risk assessment and early warning systems for climate-related health impacts.
- 2. Evidence-Based Policies, Strategies, and Capacity Building
- Foster multi-sectoral collaboration and inclusive governance for policy implementation.
- Emphasize health education, particularly for vulnerable populations, regarding climate impacts.
- 3. Innovation, Production, and Digital Health
- Support the development of climate-resilient health infrastructure and services.
- Encourage research in health technologies, ensuring equitable access and sustainability in healthcare products.
- 1. Surveillance and Monitoring
- Reporting and Coordination
- Continuous monitoring through voluntary party reporting to the WHO, utilizing health-related indicators to ensure accountability.
The Allegations of Deliberate Mishandling of AQI Data by the Government
Some critics have pointed out that the push for EVs in India may have led to the deliberate mishandling of AQI data. It is alleged that certain stakeholders with vested interests in promoting electric vehicles may have manipulated the data to create a sense of urgency and crisis around air pollution levels.
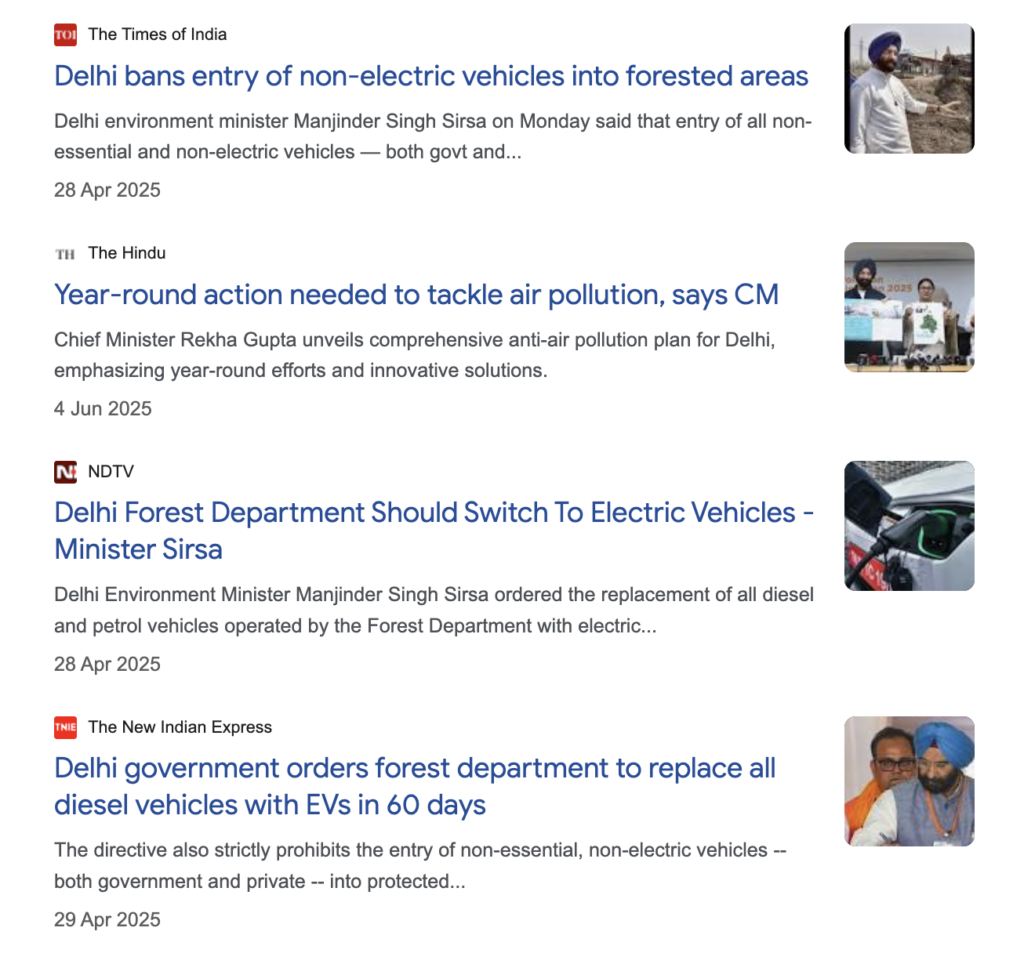
Delhi Environment Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa advocates for electric vehicles (EVs) as a key measure to combat pollution and has announced several related policies.
His statements and actions include:
- Transitioning public transport: He has stated that nearly 90 per cent of Delhi’s public CNG buses will be phased out by December 2025 and replaced with electric buses.
- Banning non-electric vehicles in sensitive areas: He announced an immediate prohibition on the entry of all non-essential and non-electric vehicles (both government and private) into forest and protected areas, such as the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Mandating government transition: He directed the complete replacement of all diesel and internal combustion engine vehicles operated by the forest department with EVs within 60 days, to promote “quiet, clean mobility”.
- Promoting EV adoption in general: Sirsa has spoken about the Delhi government’s EV Policy 2.0, which aims to encourage the adoption of EVs, particularly two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and goods carriers, with a target of 95 per cent of all new vehicle registrations being electric by 2027.
- Restricting older vehicles: As part of broader anti-pollution measures, the government is enforcing a ban on refuelling petrol vehicles older than 15 years and diesel vehicles older than 10 years, which encourages the transition to cleaner, electric alternatives.
Electric Vehicles in India: Balancing Growth with Urgent Safety Concerns
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India has unfortunately been accompanied by a rise in accidents and fire incidents, raising significant safety concerns. Data from various sources highlight this troubling trend, with thousands of incidents reported across the country in recent years.
In 2024 alone, India recorded over 7,500 EV-related accidents nationwide, a substantial increase from approximately 4,300 in 2022, according to government data. Gujarat, a state within India, reported 211 EV accidents in 2024, resulting in 76 fatalities and 188 injuries. This trend reflects a consistent acceleration over the past three years, closely mirroring the surge in EV sales. In 2022, Gujarat experienced 125 EV accidents with 24 fatalities, which then spiked to 208 accidents and 62 deaths in 2023. Karnataka has also seen a significant number of incidents, with 83 EV fire cases reported between January 2020 and November 2024. The highest number of these incidents occurred in 2024 (36 cases), followed by 2023 (28 cases).
Causes of EV Fires and Accidents Several factors contribute to the prevalence of EV fires and accidents in India:
- Battery-related issues: The primary culprit behind EV fires is often the lithium-ion battery. When these complex and sensitive batteries experience issues, a process called thermal runaway can occur. This involves cells overheating and releasing flammable gases, which can ignite nearby cells, leading to temperatures exceeding 600 degrees Celsius and potentially resulting in smoke, flames, or explosions.
- Mechanical damage: Even minor impacts can destabilize battery cells. Studies have shown that an axial displacement of just 2.3 mm can cause highly charged batteries to fail. An example of this was a Tata Nexon EV that caught fire at a service centre after being involved in an accident where it fell into a pit, with the service centre attributing the fire to battery damage.
- Environmental stress: India’s harsh climate, with summer temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius, exacerbates the risk. Heat accelerates chemical reactions within batteries, while moisture can damage cells, and dust can block cooling vents.
- Substandard manufacturing and components: Many early EV two-wheelers were assembled with substandard batteries, leading to fire incidents. The quality of manufacturing varies widely, and two-wheelers and three-wheelers, which are common in India, often face tough conditions and may use parts that are not up to standard.
- Inadequate Battery Management Systems (BMS): Many cheaper electric vehicles have BMS that do not effectively monitor real-time changes in voltage or temperature, failing to detect problems before they become critical.
- Poor cooling systems: Design flaws such as a lack of ventilation and poor materials in cooling systems can make batteries more dangerous. Electric cars and trucks generally have more sophisticated designs with advanced cooling systems compared to e-scooters and e-bikes, which face a higher risk due to poor-quality battery design and construction.
- User negligence: Using unapproved chargers or ignoring warning signs like battery swelling can also contribute to incidents.
- Power leakages and short circuits: In Karnataka, 65 of the 83 fire incidents were attributed to power leakages, and 13 to battery explosions. A suspected short circuit at a charging point in the basement of a commercial complex in Yelachenahalli, Bengaluru, resulted in 19 electric vehicles, mostly bikes, being gutted.
- Workshop repairs: Incidents can also occur during workshop repairs, as seen with the Tata Nexon EV fire.
Ref:
- Inspired by India’s efforts to curb carbon emissions: Bill Gates. [ https://m.economictimes.com/news/india/inspired-by-indias-efforts-to-curb-carbon-emissions-bill-gates/articleshow/92023434.cms ]
- Bill Gates says inspired by India’s efforts to curb carbon emissions. [ https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/bills-gates-says-inspired-by-indias-efforts-to-curb-carbon-emissions-3041016 ]
- India must set example in climate crisis fight: Bill Gates. [https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-must-set-example-in-climate-crisis-fight-gates-101613422213615.html ]
- Bill Gates: How we’ll move around in a clean, green future. [ https://www.weforum.org/stories/2020/08/carbon-emission-electric-vehicles-biofuels-elctrofuels/ ]
- India’s culture of innovation always inspires me. [ https://www.linkedin.com/posts/williamhgates_indias-culture-of-innovation-always-inspires-activity-7164312021444780034-PbGN ]
- https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/climate-change/en—belem-action-plan.pdf#:~:text=This%20Plan%20provides%20a%20framework,hereinafter%20referred%20to%20as%20’Endorsing
- Rise in EV accidents, ’24 saw 76 fatalities. [ https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/rise-in-ev-accidents-24-saw-76-fatalities/articleshow/119881466.cms ]
- India’s EV Fire Problem: Can Battery Intelligence Fix It Before It Escalates? [ https://www.evmechanica.com/indias-ev-fire-problem-can-battery-intelligence-fix-it-before-escalates/ ]
- Tata Nexon EV Electric Car Burns At Service Centre. [ https://www.ndtv.com/auto/tata-nexon-ev-electric-car-burns-at-service-centre-8162041 ]
- EVs on fire: Karnataka reports 83 cases since 2020; Okinawa, Ola top list. [ https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/bangalore/evs-fire-karnataka-okinawa-ola-report-cases-9734275/ ]
- EV vehicles gutted in accidental fire. [ https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/ev-vehicles-gutted-in-accidental-fire/article70117746.ece ]
- Electric car catches fire in Bengaluru: Here’s what causes EV fires and why electric two-wheelers are at higher risk. [ https://m.economictimes.com/industry/renewables/electric-car-catches-fire-in-bengaluru-heres-what-causes-ev-fires-and-why-electric-two-wheelers-are-at-higher-risk/articleshow/104081291.cms ]
Also Read:
