- When today’s customers think of banking, the first thing that comes to their mind is online or digital banking.
- However, even though the terms online banking and digital banking are used interchangeably, they are not the same.
- In this article, we explore digital banking as a concept and understand the distinct traits of a truly digital bank.

The unanticipated global pandemic caused a shift to the digital era for all kinds of businesses. Banking is no exception. In the last few years, the number of consumers visiting a bank branch for banking services has dwindled quite a bit. In this article, let’s reflect a bit on how digital banking is revolutionizing the banking industry.
When one considers the digitalization of global banking infrastructure, a terminology that comes first into mind – is “online banking”. How is it different from digital banking? People sometimes use words a bit loosely without clearly understanding their meaning. This is why many people confuse digital banking and online banking.
In reality, they are two separate concepts. In the case of online banking, the core aspects of a bank are made available online. These include deposits, withdrawals, fund transfers, and bill payments. But for anything more than this, you have to visit a branch. Hence, online banking is a technology that goes hand-in-hand with branch-based banking.
In the case of digital banking, the entire banking service is made available through the internet. You can access the digital bank through an app or its website. All operations that a consumer avails through a traditional bank branch can be availed through the app. It embraces the automated processing of requests from consumers and removes the hassle of paperwork completely. In digital banking, a high level of process automation is present and includes application programming interfaces (APIs) for cross-institutional services. Financial data can be accessed through desktops, mobile phones, or ATMs.
A brief history of Digital Banks
Digital banking is not a brand-new technology that came into existence in the last few years. The green shoots of digital banking technology emerged in the ‘60s, with ATMs and cards that were dubbed as “e-banking” in many countries. Then in 1994, Microsoft Money, a personal finance management program, incorporated online banking. That was when thousands of households started accessing banking services online. The first digital-only banks were established in 1997 and 1998 in Canada and USA respectively. These banks were Tangerine (Canada) and First Internet Bank (USA).
With the proliferation of faster internet connectivity, digital banking has become a modern-day phenomenon now. As of 2020, over 76% of consumers receive their banking services through digital banks.
Distinct traits of a truly Digital Bank
A digital bank is not the result of a functional website or an app. It’s much more than that. There are a few fundamental aspects that are very important for every digital bank.
1. 24×7 invisible banking:
Banking is evolving rapidly today. Hence, digital banks should be able to provide an anytime/anywhere experience to their consumers without needing physical presence. This essentially eliminates filling up paper forms and standing in queues. Banks have now started doing e-KYC through voice, video, and biometrics.
2. Data aggregation:
Digital banks should be capable of utilizing data more effectively. Successful digital banking corporations use data to provide a more personalized experience to their consumers. This is made possible by analyzing spending patterns, repayment obligations, and other data.
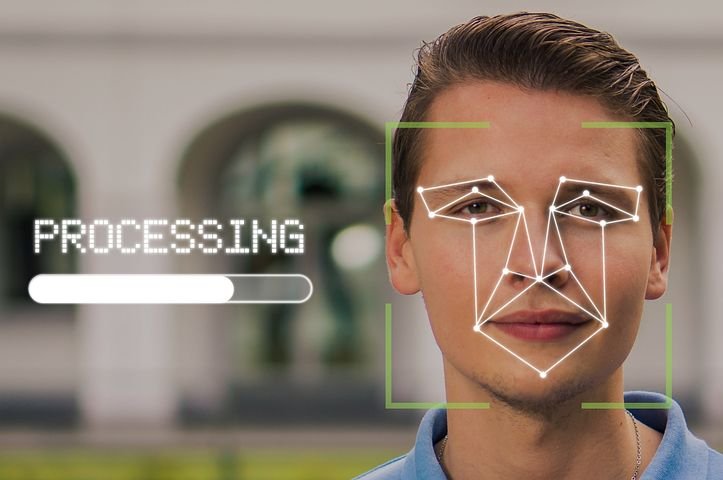
As an example, a bank in Slovakia is doing customer onboarding using a third-party mobile application. This makes it 70% faster than the process followed by normal banks. They use neural networks, biometrics, and machine learning for doing identity verification of customers. Authentication is done through customer device cameras and biometric technology to track eye movements, facial features, and light conditions.
3. Open banking:
Open banking acts as the backbone of data aggregation. Through this, banks are now able to augment customer information through third-party vendors, like retailers or utility companies.
4. Security:
Security is quite an important aspect of banking. New-age security in the banking system is characterized by multiple layers, two-factor authentication, identity verification, facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition.
Digital banking is clearly a reality that is continuing to disrupt the financial world. In the coming years, a combination of blockchain and P2P could cause market decentralization. Also, big tech companies will continue to digitize banking platforms. Moreover, challengers and neo-banks, which are small now, will grow to rule the banking market.
It’s clear that digital banking is here to stay. Question is, how do we as service providers help our clients embark on that journey?
Source: BusinessInsider
