Geoengineering Affects You, Your Environment, and Your Loved Ones..
A startup says it’s begun releasing particles into the atmosphere, in an effort to tweak the climate
A startup claims it has launched weather balloons that may have released reflective sulfur particles in the stratosphere.
David Keith:
“You can actually spray sulfuric acid in the stratosphere
20 kilometres above our heads
And use that to stop the planet warming …
If you close your eyes, imagine airplanes dispersing sulphuric acid in the lower stratosphere. Sulphur combined with water vapour creates minute sulphate aerosols when released. By reflecting about 1 percent of the sun’s energy back into space, the aerosols will cool the planet a tiny bit.
David Keith admits geoengineering SRM ( Solar Radiation Management) will kill many tens of thousands of people per year.
David Keith Admits Many Thousands will Die from Harvard Solar Geoengineering Program 2018
Pilots, Doctors and Scientists Tell the Truth About Chemtrails
Kristen Meghan – Former Air Force 2014

Related Article:
Mexico has become the first-known country in the world to move to ban solar geoengineering activities.
How Two Weather Balloons Led Mexico to Ban Solar Geoengineering

MEXICO CITY, March 27, 2023 (Reuters) – On an April day, the founder of a U.S. startup called Make Sunsets stood outside a camper van in Mexico’s Baja California and released two weather balloons containing sulfur dioxide into the air, letting them float towards the stratosphere.
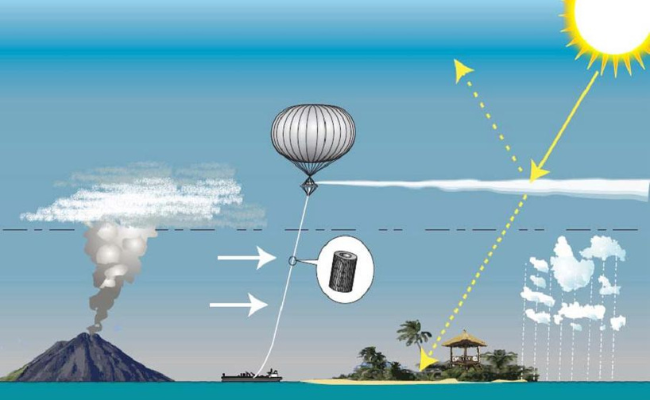
Entrepreneur Luke Iseman said the sulfur dioxide in the balloons would deflect sunlight and cool the atmosphere, a controversial climate strategy known as solar geoengineering. Mexico said the launch violated its national sovereignty.
While the Mexican government announced its intention to ban solar geoengineering in January, its current actions and plans to discuss geoengineering bans with other countries have not been previously reported.
“Progress is being made… to prepare the new regulations and norms on geoengineering, that is, to advance an official Mexican standard that prohibits said activity in the national territory,” Mexico’s environment ministry said in a written statement to Reuters.
The backlash from Mexico arrives as growing numbers of scientists and policy makers are urging further study of solar geoengineering, recognizing that emissions cuts alone will not limit dangerous climate change and that additional innovations may be needed.
GLOBAL GEOENGINEERING BAN
Climate policy experts said Mexico is in a position to help set the rules for future geoengineering research.
“A country like Mexico could start pulling together other countries and say: ‘Let’s work on this together and see how we can ban it together or make it happen properly together,’” said Janos Pasztor, executive director of the Carnegie Climate Governance Initiative (C2G), which advises on governance of solar geoengineering and other climate-altering technologies.
The Mexican environment ministry statement said it would explore using the Convention on Biological Diversity’s call for a moratorium on “climate-related geoengineering activities” to enforce its ban.
Agustin Avila, a senior environment ministry official, told Reuters Mexico will also try to find common ground with other countries on geoengineering at the COP global climate summit in the United Arab Emirates this year.
The Mexican government said Make Sunsets’ balloon launch highlighted the ethical problems of allowing private companies to conduct geoengineering events.
“Why is this company, located in the United States, coming to do experiments in Mexico and not in the United States?” said Avila.
Iseman told Reuters in an email he chose Mexico because “most researchers report that particles launched into the stratosphere near the tropics will create more cooling by staying up longer.” Also, he had a truck and camper in Baja and thinks the region is beautiful, he wrote.
David Keith, a professor of applied physics and public policy at Harvard University who has dedicated much of his research to solar geoengineering, called Iseman’s launch a “stunt.”
Iseman has a background in business, not science, but said he consulted with climate scientists. Other innovative startups were ridiculed in their early days, he said. “If the ‘responsible experts’ were solving the problem, we wouldn’t have to,” he said in an email.
Until Mexico’s dispute with Make Sunsets, solar geoengineering had been gaining attention from policy makers and scientists as a possible solution to climate change, and limited research funding.
The strategy, also known as Solar Radiation Management, seeks to mimic the natural cooling effects of volcanic eruptions when ash clouds reflect back enough sunlight to reduce the warming of the earth by using planes or balloons to disperse tiny particles in the stratosphere.
Last month, 60 scientists including former NASA climate scientist James Hansen signed a letter in support of further research.
The Degrees Initiative, a UK-based non-government group, awarded $900,000 for research into the impacts of solar geoengineering on weather patterns, wildlife and glaciers to scientists from Chile, India, Nigeria and other countries.
The U.N. Environment Program in late February also recommended further study of geoengineering.
Yet some scientists remain opposed to further research, arguing that large-scale interventions in the atmosphere risk triggering extreme and unpredictable weather changes, including major droughts that would severely impact agriculture and food supply.
In 2021, the Swedish government grounded a Harvard-led study by Frank Keutsch and Keith, which planned to spray calcium carbonate dust into the atmosphere to deflect sunlight after indigenous Saami people accused researchers of lacking respect for “Mother Earth.”
Frances Beinecke, a veteran environmental activist and board member of the Climate Overshoot Commission, a think tank focused on developing strategies to reduce the risk of overshooting 1.5 C in warming, said the Make Sunsets episode underscores the urgency of developing a regulatory framework that would allow further study of geoengineering and set safe and equitable rules for its use.
“The Mexico example illustrated to us that it’s not only governance to consider whether or not to utilize it, but you need governance in the research phase,” she said. “People can’t just go all over the world and launch field experiments without some kind of oversight.”
Iseman said he would welcome clearer regulation but that the international community is moving “too slowly.”
Mexico has not set a date for implementing its ban, a spokeswoman for the environmental ministry said.
And it’s unclear what effect a ban might have. Keith argues a ban is unenforceable. “You can’t write legislation that says you can’t put sulfur in the stratosphere since every commercial flight does that,” he told Reuters.
Others note that a ban on geoengineering on Mexico’s territory would offer no protection from the planet-scale impact of future experiments by any of its neighbors.
“It could happen literally next door. In terms of impacts on the world, it’s the same,” Pasztor said
Meanwhile, Make Sunsets said in a Feb. 21 blog post it had performed three additional launches near Reno, Nevada.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said Make Sunsets did not report the launches. “The Weather Modification Act requires that any activity performed with the intention of producing artificial changes in the composition, behavior, or dynamics of the atmosphere be reported to the NOAA Weather Program Office before the commencement of such project or activity,” NOAA told Reuters.
Iseman said he did seek clearance from the Federal Aviation Authority, but did not disclose the balloons contained sulfur dioxide. “As far as I can tell, there isn’t any rule that would require us to do so – or even anyone who it would be relevant to notify,” he said.
(This story has been corrected to say that David Keith was involved in the Harvard study, not lead it, in paragraph 23)
Source: Reuters, Twitter, Rumble, MIT Technology Review, Wikipedia
Also Read:
US Presidential Candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. and Dane Wigington: Is Climate Engineering Real?
